Multimode optical fiber transmission performance is mainly limited by the phenomenon of DMD multimode fiber. Multimode optical fiber in the transmission during the pulse, an optical pulse broadening will diverge when such severe divergence condition to a certain extent, between the front pulse is superimposed on each other, so that the receiver can not accurately distinguish each of the optical fiber pulse signal, this phenomenon we called DMD (Differential Mode Delay).There are two main reason, first, the core refractive index distribution is not perfect. Multimode fiber cables DMD is the combined effect of the dispersion characteristic of the propagation time between the different radial positions of the incident pulse and the optical mode, the index multimode fiber refractive index profile can be designed well DMD characteristics. But DMD of refractive index profile is very sensitive to small deviations, and therefore it must be very precisely controlled in multimode fiber production, to achieve the perfect design values of the refractive index profile distribution. Second, the fiber central depression. A central depression is the refractive index of the fiber core center of decreased phenomenon. This recesses is connection with optical fiber manufacturing process. This will affect the transmission characteristics of the central depression of the fiber, the fiber properties decrease.
Therefore, precise control of the refractive index profile of the fiber and the elimination of the central depression is 10Gb / s Ethernet multimode fiber (OM3 fiber) R & D and production of the main tasks. MCVD and PCVD process is more suitable for the production of OM3 fiber preform. PCVD is the preferred method of manufacturing a multi-mode optical fiber having a number of layers deposited, precise control of the cross-sectional characteristics, the deposition process thousands layer can effectively control the doping amount of the deposited layer to obtain a refractive index distribution required to comply with the theoretical. While the process of collapsing, the recess etching amount by controlling the appearance of pore size can be avoided and the central hub.
10Gb / s Ethernet standard IEEE802.3ae get through, it will a 10Gb / s Ethernet market presented. Development in line with standard Gigabit Ethernet communication products is imperative. Long Fei, Draka, Corning, OFS have been successfully developed in line with TIA/EIA-4Array2AAAC standard 50/125mm laser optimized multimode graded-index optical fiber distribution products. Full bandwidth and DMD injection test results show that the 850nm wavelength, the optical fiber can support the transmission distance of 300 meters above the 10Gigabit network system. Meanwhile, the fiber also supports 10Gigabit Fibre Channel abd 10Gigabit of the OIF (Optical Internetworking Forum) standards, and is compatible with low-rate LED light transmission network.
With the rapid development of FTTx, a large multi-mode optical fiber into the interior, in the indoor environment and the narrow wiring, fiber is subjected to high bending stresses, especially in applications where long fibers are usually more compact wound storage box, it will be under a lot of fiber bending stress. With this, the attenuation properties and mechanical resistance to bending the cable put forward higher requirements. To solve these problems, bend-insensitive multimode fibers into being, similar bend insensitive singlemode fiber (G.657), it becomes a major field of research focus on multi-mode fiber.
In recent years, Draka, Corning, OFS has released OM3/OM4 bend-insensitive multimode fiber products. The fiber is compatible with the current conventional OM3/OM4 multimode fiber and optical fiber refractive index profile by optimizing the design, greatly reduces the fiber macrobend additional attenuation, minimum bend radius is generally up to 7.5mm. OM3/OM4 uses bend insensitive multimode fiber patch cables in a way interior simplifies installation, reducing installation costs and reduce the risk of system interruption or failure. Since the bend-insensitive OM3 / OM4 multimode fiber has many advantages, once launched, it was favored on the market of all ages.
As we know, whether single-mode or multi-mode optical fiber, the numerical aperture (NA) is larger, the better its anti-bending performance. This is because the numerical aperture (NA) is greater, the difference by which the core and cladding refractive index is greater, the stronger the fiber waveguide ability. In a multimode fiber, the refractive index difference between the core of the fiber 62.5μm is twice the fiber core 50μm, and therefore the latter bending performance is poor, because the basic pattern of the fiber core 50μm Design is fixed, unable to improve its performance by increasing its resistance to bending refractive index difference. In the design of the fiber, due to lower Young’s modulus of the inner layer of the coating material, the outer layer of the coating material to increase the Young’s modulus is effective in improving the bending resistance properties. Furthermore, due to lower glass transition temperature Tg of the inner layer of coating material can be improved fiber bending properties at low temperatures. However, in order to more effectively improve the core 50μm anti-bending performance multimode fiber, the fiber must find a way out design from a structure (refractive index profile) .
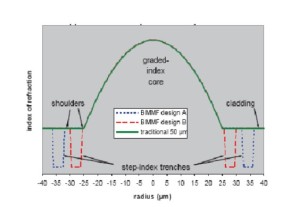
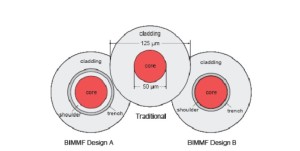
Bend-insensitive multimode fibers OM3/OM4 structure is similar to the standard multimode fiber, bend-insensitive multimode fibers (bend insensitive multimode fiber, BIMMF) the refractive index profile shown in Figure 12. Wherein the green line is a conventional 50μm multimode graded index profile of the optical fiber, blue and red dotted line for bend-insensitive optical fiber in two designs, the three-section of a multimode optical fiber shown in Figure 13. BIMMF distribution index profile, and the same in the core region 50μm conventional multimode fiber, only the ring groove is provided in the region depressed refractive-index cladding region near the core (called trench-assisted multimode fiber ). In conventional multimode fiber, when the fiber bend radius is too small, light intensity conduction mode will escape the core, causing signal distortion. In the bend-insensitive multimode fiber, the refractive index of the ring groove type subsidence area will form an obstacle to escape the intensity wakefield core barriers, thus effectively reduce the fiber macro bending loss.
Figure 12 50μm multimode fiber refractive index profile
Figure 13 Conventional 50μm multimode fiber bend insensitive MMF, and two cross-sectional view BIMMF
The Multimode Fiber Proucts on market
FC-FC Duplex 62.5/125 OM1 Multimode Fiber Patch Cable
FC-SC Simplex 50/125 OM2 Multimode Fiber Patch Cable
BIMMF bend-insensitive fiber mode field shown in Figure 14: In the conventional multimode fiber MMF, the guided mode in strong low conductivity state, and in close proximity to the core – cladding interface propagating order modes, because the effective refractive index neff close to the refractive index of the cladding n2, it is weakly conducting state (when the guided mode is equal to the effective refractive index neff cladding refractive index n2, the mode cutoff). Conduction state is weak order modes in the fiber bend radius is too small, its intensity will escape the core, causing signal distortion. In the bend-insensitive fiber BIMMF ring depressed trench type refractive index distribution has two light guide interface, the refractive index in the descending interface, the interface to form a light guide. Because of this interface, enhanced guided mode fiber core conductivity, so that the original order modes weak to lead the state into a strong lead state, shown in Figure 14. In addition, the external interface subsidence ring groove type refractive index distribution of the refractive index of small to large, the formation of refractive interface. Since the refractive index profile of this special structure, there is a leakage conductivity mode (leaky mode) in BIMMF fiber. Leakage mode is the solution of the equation in the intrinsic region outside the cutoff, leaky guided mode parsing mode is outside the cutoff continuous, their field is the same, but its intrinsic value, or the propagation constants are complex solutions Eigenequation, thus There are inherently leaky mode attenuation can not normally spread dissemination. The effective refractive index neff leakage mode of the cladding is less than n2. In the conventional multi-mode fiber, a leaky mode consumption decline rapidly, since the refractive index of a conventional optical fiber structure can not support its propagation in the fiber. And it BIMMF fiber, the refractive index in the form of this particular cross-sectional structure, a strong core to maintain close – cladding interface order modes propagating conductivity, thus effectively improve the flexural properties of the fiber.