Contaminated fiber optic cables can often lead to degraded network performance or even failure of the whole system. As such, to ensure that fiber optic cables can yield the best possible results of network performance, and it’s of great significance for network engineers to keep in mind how to handle fiber optic cables. Do you have any ideas? This text gives the guide to fiber optic cable handling rues.
Before delving into how to handle fiber optic cables, introduction to their makeup elements is required.
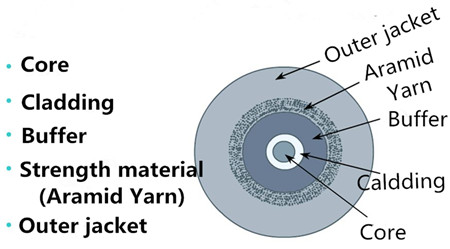
Fiber optic cable generally consists of fiver elements (figure shown above): the optic core, optic cladding, a buffer material, a strength material and the outer jacket. Commonly made from doped silica (glass), the optic core is the light-carrying element at the center of the cable. Surrounding the core is the optic cladding, whose combination with the core makes the principle of total internal reflection possible. Surrounding the cladding is a buffer material used to help shield the core and cladding from damage. A strength material surrounds the buffer, preventing stretch problems when the fiber cable is being pulled. The outer jacket is added to protect against abrasion, solvents, and other contaminants.
The outer jacket on fiber optic patch cord is often color-coded to indicate the fiber types being used. For instance, multi-mode fiber (MMF) is usually in orange to distinguish from the color yellow for single-mode fiber (SMF) through which fiber optic transceivers realize relatively long distance, such as MGBLX1. This Cisco 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver is able to achieve 10km link length over SMF.

Despite its outer protection mentioned above, fiber optic cable is still prone to damage. In such as case, a series of fiber cable handing rules are made to ensure that a cable is handled properly, so as to maintain the optimized performance, minimum insertion loss and safe working environments.
Rule 1: The exposed fiber end from coming in contact with all surfaces should be protected. If you contact the fiber with hard surfaces, then the end of it shall be scratched or chipped, causing the degraded performance.
Rule 2: It’s highly recommenced to lean the connector (plug) end each time it is inserted into an adapter, since since a dirty connector will contaminate an adapter.
Rule 3: If a fiber needs to be pulled, use the connector strain relief. Directly pulling on the fiber may result in the glass breaking.
Rule 4: It’s ill-advised to use your hands to clean a fiber work area. If you use your hands to wipe clean a work area, a piece of glass may get lodged into your hands. Considering the size of the glass, this glass may not be visible to the naked eye, bringing about eye damage.
Rule 5: If possible, always keep a protective cap on unplugged fiber connectors, because covering the adapters and connectors will help to avoid contamination and collection of residue. Besides, store unused protective caps in a resealable container in order to prevent the possibility of the transfer of dust to the fiber. Locate the containers near the connectors for easy access.

Rule 6: It’s suggestible to use fiber-cleaning materials only once. If optic grade wipes are used to clean the fiber end, they should be discarded immediately after the fiber surface has been wiped to avoid contamination.
Rule 7: The minimum bend radius of the fiber optic cable must be maintained. Surpassing the bend radius may cause the glass to fracture inside the fiber optic cable. Equally, to cause a twist of the cable is also not proposed.
Rule 8: Never look into a fiber while the system lasers are on. Eye damage may occur if you stare directly at a fiber end which is working. Always make sure that the fiber optic cables are disconnected from the laser source, prior to inspection.
After discussion, these handling rules may help you to deal with fiber optic cables and improve your network performance.
Proper handling procedures for fiber optic cables are needed to eliminate the possibility of being contaminated or damaged, and provide a clean environment for the network system. Fiberstore supplies many different types of fiber optic cables with high quality for various applications, like MTP cable. You can visit Fiberstore for more information about fiber optic cables.
