Link aggregation, as its name indicates, is the approach to combine multiple parallel physical network links into a single logical link to increase bandwidth and create resilient and redundant links. It enables us to enhance the capacity and availability of the connections between devices using Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet technology. LACP, known as link aggregation control protocol, is the standard protocol supported by IEEE 802.3ad to configure link aggregation. This article will shed some lights on link aggregation and LACP technology.
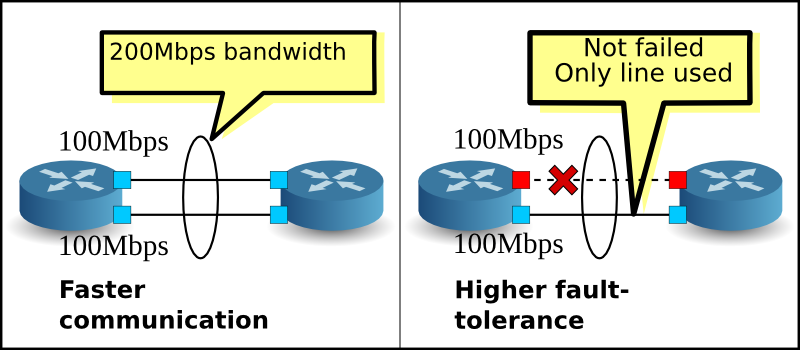
Link aggregation allows one to combine multiple network connections (same data rate, duplex capability, etc) in parallel to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and to provide redundancy in case one link goes down. Besides, link aggregation load balance enables the processing and communications activity to be distributed across several links in a trunk, thus not overwhelming a single link. Moreover, improvements within the link are obtained using existing hardware, so you don’t have to upgrade to higher-capacity link technology. This technology is not just for core switching equipment such as link aggregation switch. Network interface cards (NICs) can also sometimes be trunked together to form network links beyond the speed of any one single NIC.
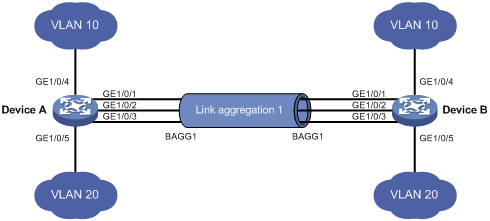
LACP is a vendor independent standard protocol for link aggregation. LACP links need to be manually configured on the physical network switch, to allow both links to appear as one logical aggregated link. LACP provides automatic determination, configuration, and monitoring member links. When LACP is enabled, a local LAG (link aggregation group) cannot transmit packets unless a LAG with LACP is also configured on the remote end of the link. A typical LAG deployment includes aggregate trunk links between an access switch and a distribution switch or customer edge (CE) device.
In a LACP enabled link, the firewall is capable of using LACP protocol to detect the physical interfaces between itself and a connected device and manage those interfaces as a single virtual interface (aggregate group) – which increases the bandwidth between devices. Enabling LACP provides redundancy within the group: the protocol can detect interface failures automatically and performs failover to standby interfaces. Without LACP, you must spend more time manually identify interface failures occurring within the channel.
By transmitting LACP packets between ports, LACP supports the automatic creation of Gigabit Ethernet port channel. It is capable of dynamically grouping port and informing the other ports. As LACP successfully identifies matched Ethernet links, it facilitates grouping the links into a Gigabit Ethernet port channel. Then it begins to change LACP packers between ports in either the two modes:
- Active—Places a port into an active negotiating state, in which the port initiates negotiations with remote ports by sending LACP packets.
- Passive—Places a port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds to LACP packets it receives but does not initiate LACP negotiation. In this mode, the port channel group attaches the interface to the bundle.
Both modes allow LACP to negotiate between ports to determine if they can form a port channel based on criteria such as port speed and trunking state. Here are some important parameters to use during configuration of the link aggregation.
LACP System Priority: This is configured per router. It is used with MAC address to create LACP System ID.
LACP System ID = LACP System Priority + MAC Address
LACP Port Priority: It is configured per port. It is used to form Port Identifier with Port Number.
LACP Port Identifier = LACP Port Priority + Port Number
It is also used to determine which port should be in standby mode during an hardware limitation.
LACP Administrative Key: It is automatically calculated equal to the channel group identification number on each LACP configured port. It defines the ability of a port to aggregate with other ports, the aggregation ability is determined by, port characteristics and configuration restrictions.
LACP Max-bundle: It is the number of bundled ports in a bundle. As I mentioned below it is maximum 8. But in some platforms it can be 4.
If all the compatible ports cannot be aggregated by LACP, then the remaining ones can act as standby ports. When there is a failure occurs in one of the bundled ports, the standby ports become active one by one.
Link aggregation is the efforts made to set up parallel network structures to provide redundancy, or to improve performance, which increases bandwidth, provides graceful degradation as failure occurs, and enhances availability. LACP facilitate the configuration of link aggregation with automatic determination, configuration, and monitoring. Hope this article could help understanding link aggregation and LACP.
Related Article: LACP vs PAGP: What Is the Difference?
