Multimode fiber systems offer flexible, reliable and cost effective cabling solutions for local area networks (LANs), Storage Area Networks (SANs), central offices and data centers. Multimode fibers support data rates from 10 and 100 Megabits per second (Mb/s) up to today’s 1 Gigabit per second (Gb/s) and 10 Gb/s applications, with standards in development to support data rates up to 40 Gb/s and 100 Gb/s.
Three types of multimode fiber are currently found in premises networks: 62.5μm multimode fiber (OM1), 50μm multimode fiber (OM2), and laser optimized 50μmmultimode fiber (OM3). 50μm and 62.5μm refer to the diameter of the fiber core, which is the area that carries light signals. For the most part, OM1 fiber is found in legacy systems. Over the past five years, network designers have migrated to 50μm fiber,especially laser optimized multimode fibers (OM3), as they can support higher data rates and longer distances. Considering the higher bandwidth advantage, and the applications that most customers will use today or in the future, the Fiber Optics LAN Section recommends that for new installations, customers install OM3 fiber.
While 50μm multimode fiber might seem new, in the 1970s, when optical fiber was introduced, standard 50μm fiber (OM2) was the most popular of the early fiber types available, and was used for both long haul and short reach applications.
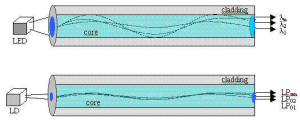
After the introduction of single-mode fiber in the 1980s for long haul telephony applications, multimode fibers were applied to short-reach interconnects, such as building and campus backbones needing support over distances from 300 meters to 2000 meters. As with many technology choices, there were trade offs between 50μm multimode and the singlemode fiber systems. The light-emitting diode (LED) sources used for multimode applications had a very large “spot” and the 50μm fiber did not fully couple the available power into the 50μm core. Consequently, 50μm fiber used with 850 nm wavelength LEDs was limited in distance. Receivers were not always able to detect an adequate light power at the distant end of the backbone. Still, network designers were reluctant to install single mode fibers as the power sources remained more expensive and there was no need in most premises applications for the long link lengths the more expensive singlemode facilities would provide.
62.5μm multimode fiber (OM1) was introduced in 1985 to solve these two problems. Because more light from LEDs could be coupled into its larger core, OM1 fiber could support 2 km campuses at 10 Mb/s. At the same time, its higher numerical aperture, which can be thought of as the fiber’s “light gathering” ability, made it easier to cable. Through much of the 1980’s and 90’s one multimode fiber, 62.5μm core FDDIfiber became a defacto standard among the vast majority of LAN installations. Despite continual upgrades in LAN bandwidth requirements, FDDI grade fiber remained a work horse for backbone fiber installations for many years, and is still present in legacy systems. Now we recommend you one type of multimode fiber patch cable from fiberstore.
Multimode fiber patch cables can be used as cross)connect jumpers, equipment and work area cords. All Signamax optical fiber patch cords are manufactured using riser) grade (OFNR) cable and are 100% factory tested for insertion and return loss to ensure transmission per formance perANSI/TIA)568)C.3 standard specifications.Patch cords terminated with ST,SC, LC and MT)RJ connectors (uniform and hybrid versions) are available in duplex and simplex designs. Our store have SC fiber optic cable, ST to ST fiber cable, ect.
Fiberstore produces high quality Fiber Optic Patch Cable using a variety of commercially available connectors and fibers. These patchcords offer low insertion losses, and excellent repeatability. Patchcords can be manufactured to any specified length. An array of cable materials are available, including unjacketed fiber, 0.9 mm outside diameter (O.D) loose tube buffer, 3 mm O.D kevlar rein-forced PVC jacketing, 3 mm armored cabling, and 5 mm heavy duty armored cabling as well as 3 mm or 5 mm Stainless Steel armored cablings.