For several years ago, when talked about fiber optic transceiver, almost most of people engaged in telecommunication industry would tell that a transceiver is a device comprising both a transmitter and a receiver which are combined and share common circuitry. Almost all fiber optic transceivers uses two fibers to transmit data between routers and switches. One fiber is devoted to transmitting data to the networking equipment, while the other one is devoted to receiving data from the networking equipment. For recent years, a new kind of fiber optic transceiver has been available — Bi-Directional transceiver (BiDi transceiver).
BiDi Transceiver Basis
BiDi transceiver is a type of fiber optic transceiver which uses WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) bi-directional transmission technology so that it can achieve the transmission of optical channels on a fiber propagating simultaneously in both directions. BiDi transceiver is only with one port which uses an integral bidirectional coupler to transmit and receive signals over a single optical fiber (see the following picture). BiDi transceivers are specifically designed for the high-performance integrated duplex data link over a single optical fiber and used in bi-directional communication applications. The BiDi transceivers interface a network device mother board (for a switch, router or similar device) to a fiber optic or unshielded twisted pair networking cable.

Working Principle of BiDi Transceiver
The difference between BiDi transceivers and the two-fiber optical transceiver mainly lies in that BiDi transceivers are fitted with WDM couplers, also known as diplexers, which help to combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. So BiDi transceivers are also called WDM transceivers. BiDi transceivers are usually deployed in matched pairs to get the work most efficiently. And the diplexers of BiDi transceivers are tuned to match the expected wavelength of the transmitter and receiver that they will be transmitting data from or to.
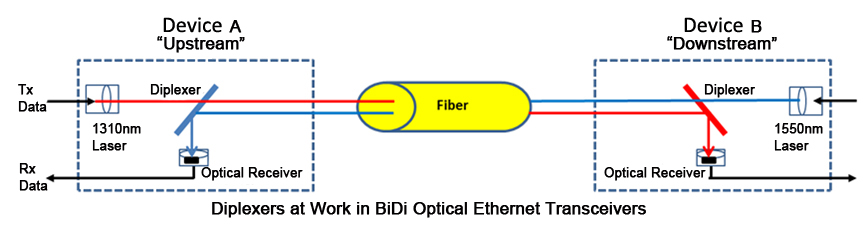
As can be seen from the following diagram, the paired BiDi transceivers are being used to connect two devices. Device A is used to get upstream data, and Device B is used to get downstream data. Tx means transmit. Rx means receive. The diplexer in one transceiver (Device A) should have a transmitting wavelength of 1310 nm and have a receiving wavelength of 1550 nm. The diplexer in the other transceiver (Device B) should have a transmitting wavelength of 1550 nm and have a receiving wavelength of 1310 nm.
Advantages of BiDi Transceiver
The decisive advantage of using BiDi transceiver is that it helps to reduce the cost of fiber cabling infrastructure. This is caused by reducing the number of fiber path panel ports as well as reducing the amount of tray space dedicated to fiber management. The deployment of BiDi transceiver enables the bandwidth capacity of the optical fiber to be doubled.
FS.COM BiDi Transceiver Solution
FS.COM supplies a series of BiDi transceivers with different types such as BiDi SFP. These BiDi Gigabit SFP transceivers support Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and Fibre Channel, etc. And they can be available for simplex SC or LC connector interface, which is used for data transmitting and receiving. Also, the BiDi SFPs are able to support a wide range of physical media from copper to long-wave single-mode optical fiber with transmission distance up to hundreds of kilometers. The most typical Tx and Rx wavelength combinations are 1310/1490 nm, 1310/1550 nm and 1490/1550 nm. FS.COM has a large selection of BiDi transceivers in stock. Choosing a FS.COM BiDi transceiver can help your fiber optic network to be most economical and efficient.
Related Article: A Brief Introduction of BiDi SFP Transceiver
