During optical transmission process, it’s no wonder that using one fiber to receive data from networking equipment, and another one to transmit data to the networking equipment. This kind of transmission mode will increase investment cost certainly. Luckily, here is a type of transceiver can solve this problem. It’s bi-directional transceiver. Today, this article will take you to make sense why BiDi transceiver can make it possible to transmit data over one fiber.
Basics of BiDi Transceiver
BiDi is short for bidirectional. BiDi transceiver is a type of fiber optic transceiver which is used WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) bi-directional transmission technology so that it can achieve the transmission of optical channels on a fiber propagating simultaneously in both directions. BiDi transceiver is only with one port which uses an integral bidirectional coupler to transmit and receive signals over a single fiber optical cable. Thus, it must be employed in pairs.
How Does BiDi Transceiver Work?
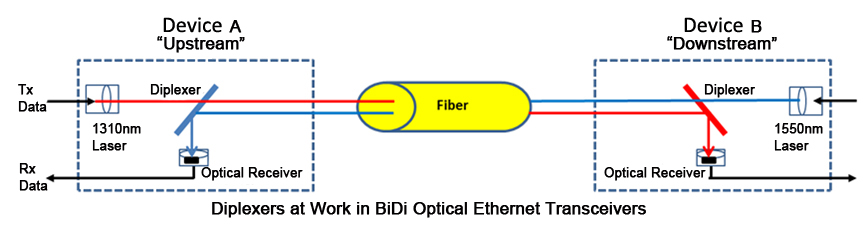
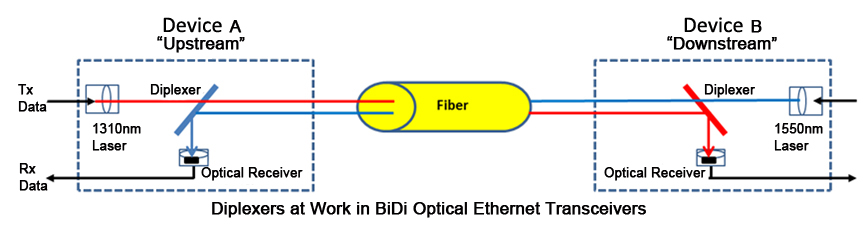
The obvious difference between BiDi transceivers and traditional two-fiber fiber optic transceivers is that BiDi transceivers are fitted with Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) couplers, also known as diplexers, which combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. For this reason, BiDi transceivers are also referred to as WDM transceivers.
To work effectively, BiDi transceivers must be deployed in matched pairs, with their diplexers tuned to match the expected wavelength of the transmitter and receiver that they will be transmitting data from or to.
For example, if paired BiDi transceivers are being used to connect Device A (Upstream) and Device B (Downstream), as shown in the figure below, then:
- Transceiver A’s diplexer must have a receiving wavelength of 1550nm and a transmit wavelength of 1310nm
- Transceiver B’s diplexer must have a receiving wavelength of 1310nm and a transmit wavelength of 1550nm
Common Types of BiDi Transceiver
BiDi SFP transceiver is typically applied for the high-performance integrated duplex data link over a single optical fiber. It interfaces a network device mother board (for a switch, router or similar device) to a fiber optic or unshielded twisted pair networking cable. And the most typical wavelength combination is 1310/1490 nm, 1310/1550 nm, 1490/1550 nm and 1510/1570 nm. This BiDi SFP transceiver is used in optical communication for both telecommunication and data bidirectional communications applications.
BiDi SFP+ transceiver is an enhanced SFP transceiver. It is designed for bi-directional 10G serial optical data communications such as IEEE 802.3ae 10GBASE-BX by using 1330/1270nm transmitter and 1270/1330nm receiver. And its transmission distance is up to 20 km.
Advantages of BiDi Transceiver
The obvious advantage of utilizing BiDi transceivers, such as BiDi SFP+ and BiDi SFP transceivers, is the reduction in fiber cabling infrastructure costs by reducing the number of fiber patch panel ports, reducing the amount of tray space dedicated to fiber management, and requiring less fiber cable.
While BiDi transceivers (a.k.a. WDM transceivers) cost more to initially purchase than traditional two-fiber transceivers, they utilize half the amount of fiber per unit of distance. For many networks, the cost savings of utilizing less fiber is enough to more than offset the higher purchase price of BiDi transceivers.
Conclusion
In summary, BiDi transceivers can combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. That is to say, to achieve the same transmitting result, it needs less money. Except for above SFP & SFP+ BiDi transceivers, FS.COM also provides 40G BiDi transceiver. This BiDi transceiver has two 20 Gbps channels, each transmitted and received simultaneously on two wavelengths over a single MMF strand (OM3 or OM4). Any one of the transceivers would meet your different application requirements with high performance.
Related Article: A Brief Introduction of BiDi SFP Transceiver