The rise of virtualisation technology has revolutionised data centres, enabling the operation of multiple virtual machines on the same physical infrastructure. However, traditional data centre network designs are not well-suited to these new applications, necessitating a new approach to address these challenges. NVGRE and VXLAN were created to meet this need. This article delves into NVGRE and VXLAN, exploring their differences, similarities, and advantages in various scenarios.
Unleashing the Power of NVGRE Technology
NVGRE (Network Virtualization using Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a network virtualisation method designed to overcome the limitations of traditional VLANs in complex virtual environments.
How It Works
NVGRE encapsulates data packets by adding a Tenant Network Identifier (TNI) to the packet, transmitting it over existing IP networks, and then decapsulating and delivering it on the target host. This enables large-scale virtual networks to be more flexible and scalable on physical infrastructure.
1.Tenant Network Identifier (TNI)
NVGRE introduces a 24-bit TNI to identify different virtual networks or tenants. Each TNI corresponds to a separate virtual network, allowing multiple virtual networks to operate on the same physical infrastructure without interference.
2. Packet Encapsulation
Source MAC Address: The MAC address of the sending VM.
Destination MAC Address: The MAC address of the receiving VM.
TNI: The 24-bit virtual network identifier.
Original Ethernet Frame: Includes the source MAC address, destination MAC address, Ethernet protocol type (usually IPv4 or IPv6), etc.
Data packets are encapsulated into NVGRE packets for communication between VMs.

3. Transport Network
NVGRE packets are transmitted over existing IP networks, including physical or virtual networks. The IP header information is used for routing, while the TNI identifies the target virtual network.
4. Decapsulation
When NVGRE packets reach the host of the target VM, the host decapsulates them, extracting the original Ethernet frame and delivering it to the target VM.
5. MAC Address Table Maintenance
NVGRE hosts maintain a MAC address table to map VM MAC addresses to TNIs. When a host receives an NVGRE packet, it looks up the MAC address table to determine which VM to deliver the packet to.
6. Broadcast and Multicast Support
NVGRE uses broadcast and multicast to support communication within virtual networks, allowing VMs to perform broadcast and multicast operations for protocols like ARP and Neighbor Discovery.
Features
- Network Virtualisation Goals: NVGRE aims to provide a larger number of VLANs for multi-tenancy and load balancing, overcoming the limited VLAN capacity of traditional networks.
- Encapsulation and Tunneling: Uses encapsulation and tunneling to isolate virtual networks, making VM communication appear direct without considering the underlying physical network.
- Cross-Data Centre Scalability: Designed to support cross-location virtual networks, ideal for distributed data centre architectures.
A Comprehensive Look at VXLAN Technology
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) is a network virtualisation technology designed to address the shortage of virtual networks in large cloud data centres.

How It Works
VXLAN encapsulates data packets by adding a Virtual Network Identifier (VNI), transmitting them over existing IP networks, and then decapsulating and delivering them on the target host.
1.Virtual Network Identifier (VNI)
VXLAN introduces a 24-bit VNI to distinguish different virtual networks. Each VNI represents a separate virtual network, allowing multiple virtual networks to operate on the same physical infrastructure without interference.
2.Packet Encapsulation
Source IP Address: The IP address of the sending VM.
Destination IP Address: The IP address of the receiving VM.
UDP Header: Contains source and destination port information to identify VXLAN packets.
VNI: The 24-bit virtual network identifier.
Original Ethernet Frame: Includes the source MAC address, destination MAC address, Ethernet protocol type, etc.
Data packets are encapsulated into VXLAN packets for communication between VMs.

3.Transport Network
VXLAN packets are transmitted over existing IP networks. The IP header information is used for routing, while the VNI identifies the target virtual network.
4.Decapsulation
When VXLAN packets reach the host of the target VM, the host decapsulates them, extracting the original Ethernet frame and delivering it to the target VM.
5.MAC Address Table Maintenance
VXLAN hosts maintain a MAC address table to map VM MAC addresses to VNIs. When a host receives a VXLAN packet, it looks up the MAC address table to determine which VM to deliver the packet to.
6.Broadcast and Multicast Support
VXLAN uses multicast to simulate broadcast and multicast behaviour within virtual networks, supporting protocols like ARP and Neighbor Discovery.
Features
- Expanded VLAN Address Space: Extends VLAN identifier capacity from 4096 to 16 million with a 24-bit segment ID.
- Virtual Network Isolation: Allows multiple virtual networks to coexist on the same infrastructure, each with a unique segment ID.
- Multi-Tenancy Support: Ideal for environments where different tenants need isolated virtual networks.
- Layer 2 and 3 Extension: Supports complex network topologies and routing configurations.
- Industry Support: Widely supported by companies like Cisco, VMware, and Arista Networks.
NVGRE vs VXLAN: Uncovering the Best Virtualization Tech
NVGRE and VXLAN are both technologies for virtualising data centre networks, aimed at addressing issues in traditional network architectures such as isolation, scalability, and performance. While their goals are similar, they differ in implementation and several key aspects.

Supporters and Transport Protocols
NVGRE is supported mainly by Microsoft, using GRE as the transport protocol. VXLAN is driven by Cisco, using UDP.
Packet Format
VXLAN packets have a 24-bit VNI for 16 million virtual networks. NVGRE uses the GRE header’s lower 24 bits as the TNI, also supporting 16 million virtual networks.
Transmission Method
VXLAN uses multicast to simulate broadcast and multicast for MAC address learning and discovery. NVGRE uses multiple IP addresses for enhanced load balancing without relying on flooding and IP multicast.
Fragmentation
NVGRE supports fragmentation to manage MTU sizes, while VXLAN typically requires the network to support jumbo frames and does not support fragmentation.
Conclusion
VXLAN and NVGRE represent significant advancements in network virtualisation, expanding virtual network capacity and enabling flexible, scalable, and high-performance cloud and data centre networks. With support from major industry players, these technologies have become essential for building agile virtualised networking environments.
How FS Can Help
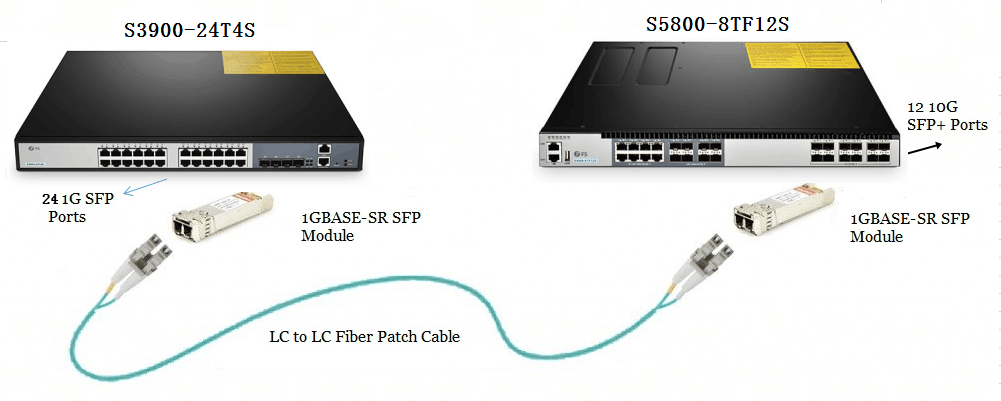
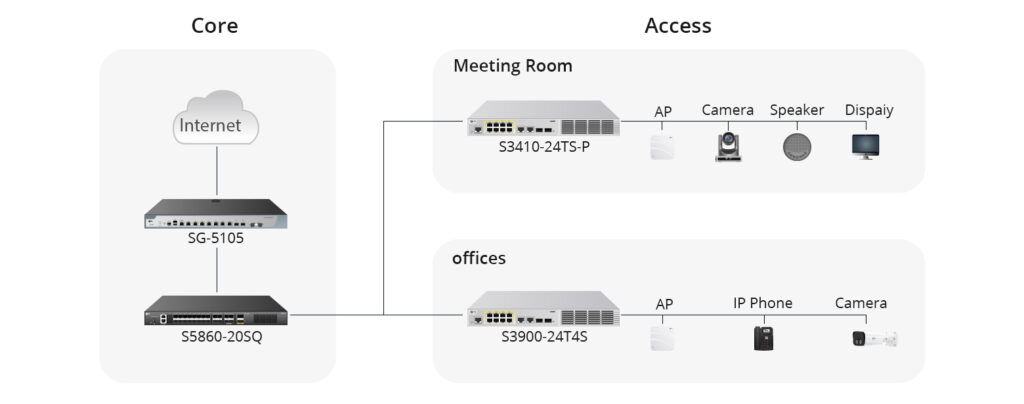
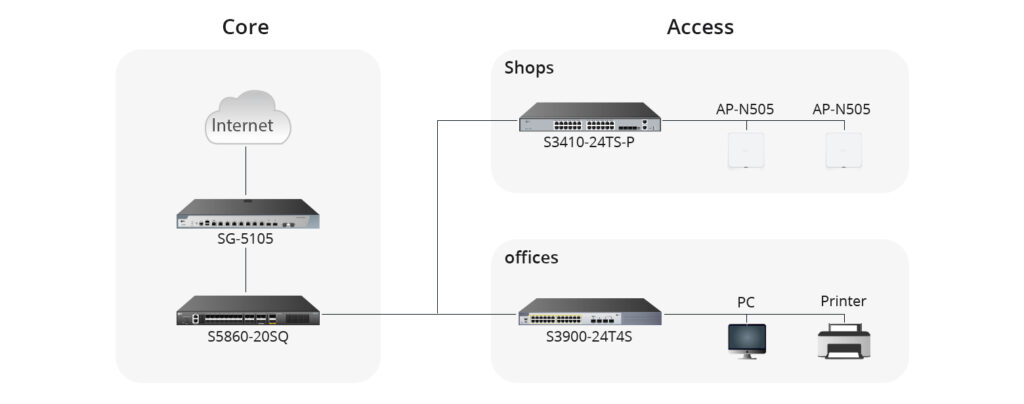
FS offers a wide range of data centre switches, from 1G to 800G, to meet various network requirements and applications. FS switches support VXLAN EVPN architectures and MPLS forwarding, with comprehensive protocol support for L3 unicast and multicast routing, including BGP, OSPF, EIGRP, RIPv2, PIM-SM, SSM, and MSDP. Explore FS high-quality switches and expert solutions tailored to enhance your network at the FS website.

















-1024x506.jpg)
-1-1024x506.jpg)