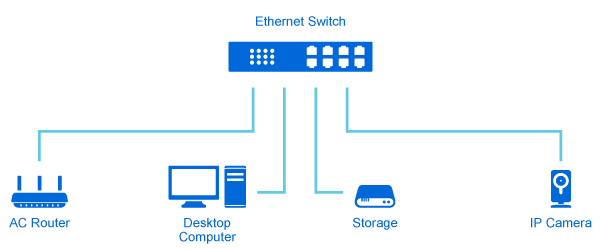
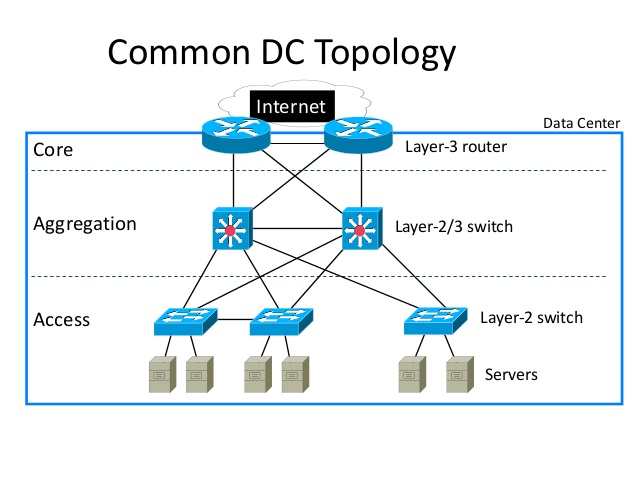
The computer switch though has long existed in the market, few people can speak on it with great familiarity. As the network expands, the computer switch grows more sophisticated and diversified. This post sheds light on the computer switch from its definition, working principle and types.
What Is a Computer Switch?
A computer switch is an Ethernet switch in nature. It is a small hardware device that links multiple PCs, printers, assess points, phones, lights and servers together within one local area network, wide area network and different network topology. Each device connected to the switch is automatically connected to and can communicate with other connected devices, as the switch is essentially designed for information exchange. So if you hook up your cable modem to a router, then connect the router to a switch, all devices plugged into the switch can access the Internet, send and receive information and approach shared resources in a smooth, highly secure, and transparent manner.
How Does a Computer Switch Work?
The computer switch doesn’t exchange information randomly but follow the specific instructions—the MAC addresses of every device. The IP packet arrives at the correct destination with the aid of the frame using MAC addresses of destination and source. It is the computer switch that shoulders the responsibility to complete process as follows.
- Learning – The switch learns the MAC address of the device on the switch port on which it receives the frame.
- Forwarding – The switch forwards message in either unicast or broadcast way. That depends on whether the destination MAC is known for sure or unknown.
- Filtering – The frame will be forwarded through that switch port only for which the switch has already learned the MAC address in its MAC table.
Common Types of Computer Switch
There are different types of computer switches available in the market. Each has different features and functions. Here introduces four common computer switches: unmanaged switch, managed switch, PoE switch and stackable switch.
UNMANAGED COMPUTER SWITCH
Unmanaged switches are typically for basic connectivity. The unmanaged network switch is common to see in our home networks or wherever a few more ports are needed, such as at your desk, in a lab, or in a conference room. It is simply a plug-and-play device that requires no configuration. The gigabit Ethernet switch in your families are mostly the unmanaged switch.
MANAGED COMPUTER SWITCH
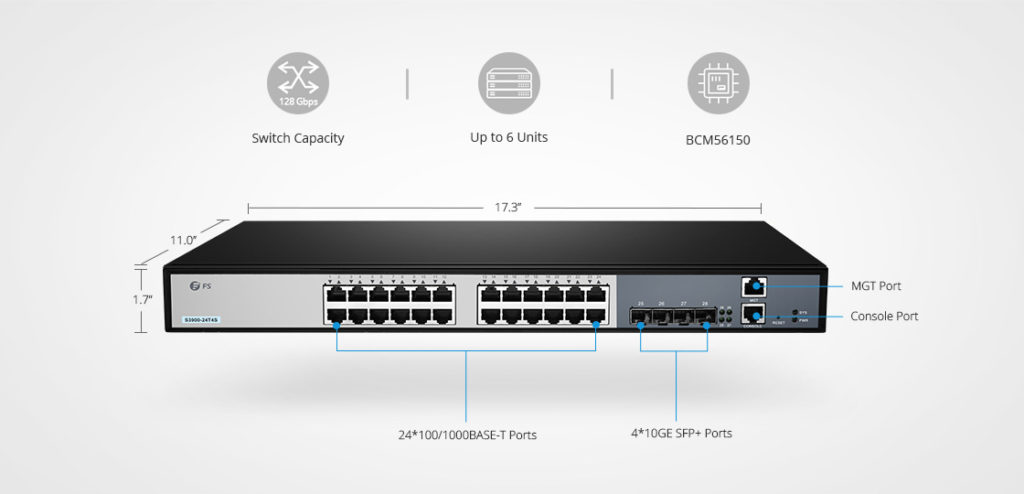
Managed switches are more advanced as they give you greater security and more features and flexibility. With this greater control, you can better protect your network and improve the quality of service for those who access the network. These can be achieved by setting a simple network management protocol or SNMP. Faster switches like 10 gigabit switch, 40 gigabit switch, 100 gigabit switch, etc are commonly working as managed switch.
PoE COMPUTER SWITCH
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch is a network switch that has utilizes Power over Ethernet technology. When connected with other devices, it can support power and data transmission over one network cable at the same time, which greatly simplifies the cabling process. FS offers PoE switches with different port numbers, ranging from 8-port, 24-port to 48-port.
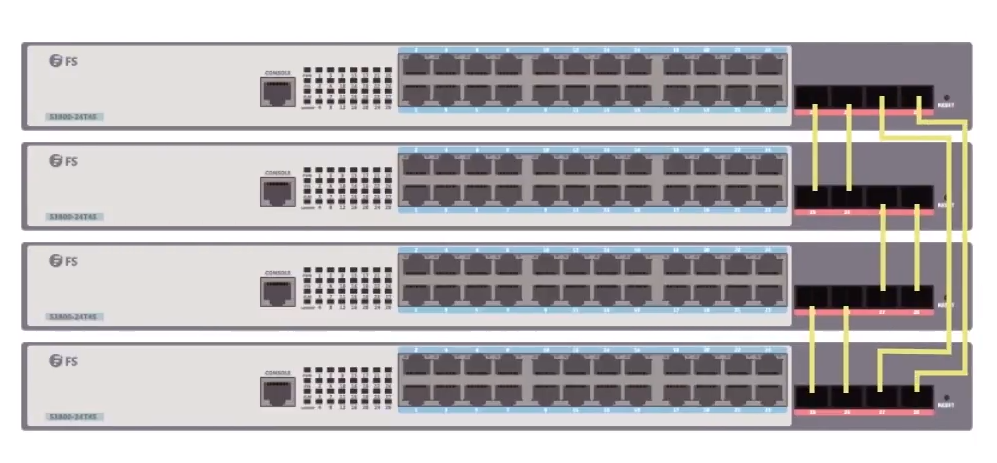
STACKABLE COMPUTER SWITCH
In the large data center, there may be many network applications and also many network switches. It poses great difficulty and triviality to the user to set and maintain each switch. Given this, stackable computer switch rises above the crowd. It enables multiple switches (usually four switches) to work as an individual unit in order to simplify the management, troubleshoot and configuration. This kind of switch can also work standalone switch.
Conclusion
The computer switch is indeed one of the important components of your networking infrastructure. FS offers plenty of fiber switches, PoE switches, or Ethernet-based switches with different port speeds. These switches are great in terms of sales, performance, and quality. To find the right computer switch, turn to our website www.fs.com and consult our expert staff if you have any questions.