Gigabit Ethernet switch is an essential part of communication systems. It is widely used as the access layer switch, which facilitates the connection of end node devices to the network. The Gigabit Ethernet switches on the market mainly differ in port and function. Then which to choose from so many options of Gigabit switches on the market? FS newly launched the S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switch. It is designed with an advanced feature set that brings high availability, comprehensive security, robust multicast control, and advance QoS to the network edge, while maintaining simple management. Let’s know more about the S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switch.
FS.COM S3900 Series Gigabit Ethernet Switch Introduction
FS.COM S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switch is advanced layer 2 plus (layer 3 Lite) Gigabit managed stackable switch with 10G uplinks, which can satisfy the demand for the future network upgrade. The S3900 series switches are the ideal Gigabit access and aggregation switch for SMB, enterprise, and campus networks. The S3900 series of switches are equipped with 24/48 ports, copper/SFP ports. All of S3900 series switches are managed stackable switches. The most distinctive characters of the S3900 series switch are listed below.
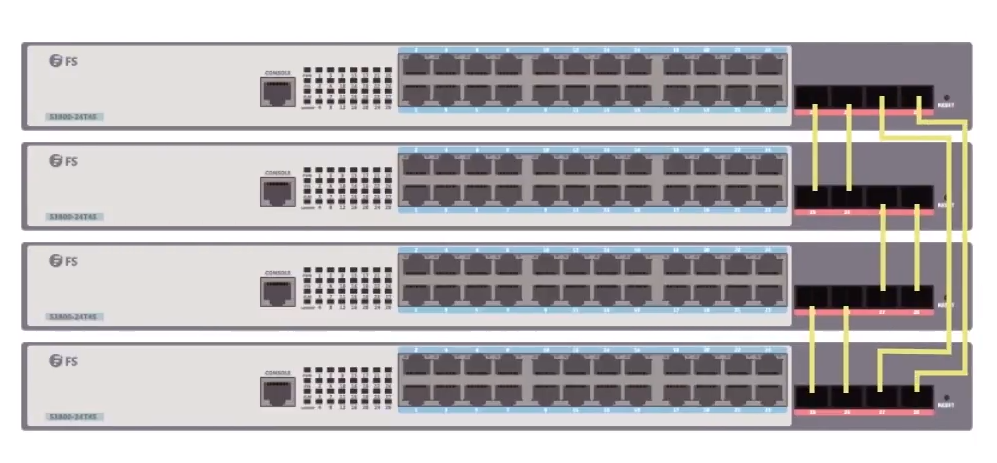
FS.COM S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switch has the switching capacity up to 128Gbps/176Gbps. It delivers wire-speed switching performance on all Gigabit ports and takes full advantage of existing high-performance Gigabit CPEs, PCs, 11n/ac Wi-Fi applications, etc. Besides, it significantly improves the responsiveness of applications and shortens file transfer time. Moreover, the 4 built-in 10G SFP+ ports provide uplink flexibility, and create 10 Gbps high-speed uplinks to 10 GbE switch or device through the connection of 10G SFP+ transceivers or 10G SFP+ DACs, thus reduce bottlenecks and increase the performance of the access network. Except for the 10G uplinks, S3900 stackable switches also have the potentiality of adding extra available ports in the future. Besides, the stackable switches which are stacked together can be managed as an entity, thus save the time and energy when you manage the stackable switches.
The design of the S3900 series incorporates high energy efficiency which can greatly expand your network capacity with much less power. The fanless design of S3900-24T4S ensures noiseless operation without disturbing your family or your staff and increases the reliability of the system. The S3900 series switch is an eco-friendly solution for your family and business network.
The S3900 switch is equipped with IGMP snooping technique which prevents the flooding of multicast traffic. The multicast traffic is forwarded to only those ports associated with an IP multicast receiver. Thus the technique reduces unnecessary load on host devices.
With industry-standard command-line interface (CLI) program, which is accessed through the console port or telnet, the S3900 series Gigabit switch provides superior management user experience. Besides, user-friendly web interface helps users to quickly and simply configure switches.
FS.COM S3900 series switch contains STP protocols. IEEE 802.1w rapid spanning tree protocol provides a loop-free network and redundant links. IEEE 802.1s multiple spanning tree protocol runs STP per VLAN base, providing layer 2 load sharing on redundant links up to 64 instances. The STP protocols prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation and also allow a network design to include backup links to provide fault tolerance if an active link fails.
Comparison of FS.COM S3900 Series Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The following chart shows the details of the three types S3900 Gigabit Ethernet switch. You can choose from them according to your actual needs.
|
Switch Type
|
S3900-24T4S
|
S3900-24F4S
|
S3900-48T4S
|
|
Ports
|
24 10/100/1000BASE-T, 4 SFP+ uplinks
|
24 SFP with 4 combo SFP, 4 SFP+ uplinks
|
48 10/100/1000BASE-T, 4 SFP+ uplinks
|
|
Switch Class
|
Layer 2+ (Layer 3 Lite)
|
Layer 2+ (Layer 3 Lite)
|
Layer 2+ (Layer 3 Lite)
|
|
MAC Address Table
|
16K
|
16K
|
16K
|
|
Jumbo Frames
|
9KB
|
9KB
|
9KB
|
|
Flash Memory
|
64MB
|
64MB
|
64MB
|
|
Stacking
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Switch Chip
|
BCM56150
|
BCM56151
|
BCM56150
|
|
Switching Capacity
|
128Gbps
|
128Gbps
|
176Gbps
|
|
Forwarding Rate
|
95Mpps
|
95Mpps
|
130Mpps
|
|
Input Power
|
100-240V AC, 50/60 Hz
|
100-240V AC, 50/60 Hz
|
100-240V AC, 50/60 Hz
|
|
Max Power Consumption
|
21W
|
43W
|
45W
|
|
With Fan or Fanless
|
Fanless
|
With Fan
|
With Fan
|
|
Price
|
US$ 280
|
US$ 400
|
US$ 410
|
Which to Choose Among S3900 Series Gigabit Ethernet Switch?
When it comes to choosing from FS.COM S3900 Gigabit Ethernet switch, you need to consider the number and type of ports you need and whether the switch is fanless or with fans.
FS.COM S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switches offer three different port combination options, which can be chosen according to your network demands.
If you need 24 port Gigabit switch, both S3900-24T4S switch with 24 10/100/1000BASE-T ports and S3900-24F4S switch with 24 SFP ports are within the scope of consideration. If cost, backward compatibility with legacy copper cabling networks, power consumption are important for you, S3900-24T4S switch is the better choice. If you prefer lower latency and switches with combo SFP ports then you could consider S3900-24F4S switch with 24 SFP ports which contain 4 combo ports. Besides, compared with S3900-24T4S switch with copper ports, S3900-24F4S switch which is connected with SFP fiber optic transceivers modules & fiber patch cables is more suitable for long-distance transmission of 550m to 150km.
If the network devices you are going to connect are of large amount, and you have a relatively big network, then you need to choose a switch with more than 24 ports. The S3900-48T4S switch with 48 10/100/1000BASE-T ports can satisfy your demand. It has the switching capacity of 176Gbps, which is the largest among the S3900 series switches.
If you are planning to use the switch in quiet space, like offices, home, shops, libraries, hospitals or clinics where noise can be an issue, FS.COM S3900-24T4S fanless switch is recommended. Fanless switches are equipped with a passive cooling system, which has the advantage of energy efficiency and lower financial cost. The switches with fans are mostly deployed in data centers which have separate data center rooms. While fanless switches are more suitable for small businesses, people working at home, and places where silence is needed.

Figure 1: FS.COM S3900-24T4S fanless Gigabit Ethernet switch
Summary
FS.COM S3900 Series Gigabit Ethernet switch has high availability, comprehensive security, robust multicast control, and advanced QoS. The article extensively discussed why you choose the S3900 series and how to choose the most suited switch for your network among the S3900 series. If you want to purchase FS.COM S3900 series Gigabit Ethernet switches or other network switch such as 10GbE switch, 40GbE switch and 100GbE switch, please contact us at sales@fs.com.