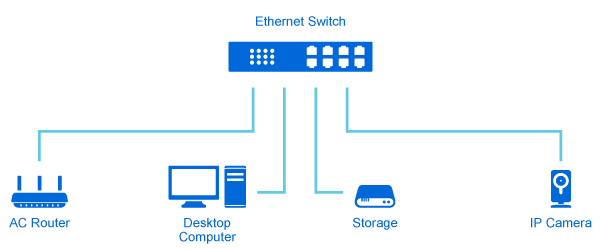
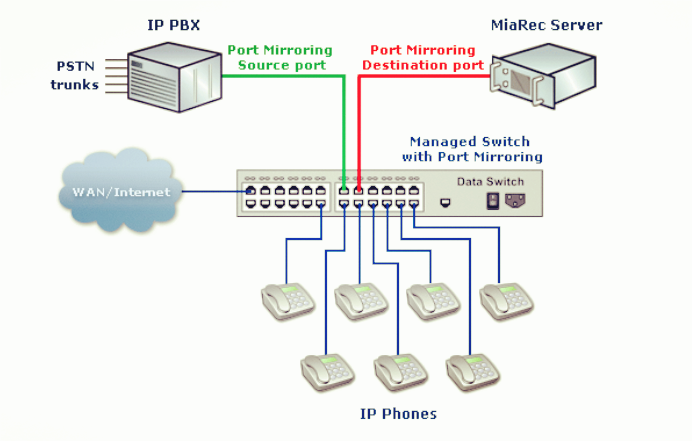
Switches are devices used in connecting multiple devices together on a Local Area Network (LAN). In terms of networking, the switch would serve as a controller, which allows the various devices to share information. Ethernet switches can be used in the home, a small office or at a location where multiple machines need to be hooked up. There are two basic kinds of switches: managed switches and unmanaged switches. The key difference between them lies in the fact that a managed switch can be configured and it can prioritize LAN traffic so that the most important information gets through. On the other hand, an unmanaged switch behaves like a “plug and play” device, which cannot be configured and simply allows the devices to communicate with one another. This blog will compare the difference between managed vs. unmanaged switch, and why would choose one over the other?
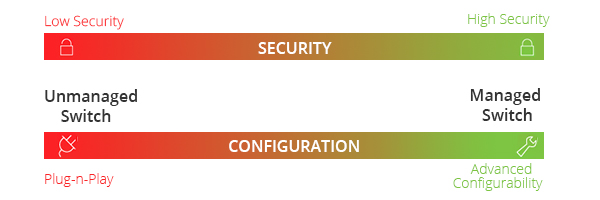
A managed switch is a device that can be configured. This capability provides greater network flexibility because the switch can be monitored and adjusted locally or remotely. With a managed switch, you have control over network traffic and network access. Managed switches are designed for intense workloads, high amounts of traffic and deployments where custom configurations are a necessity. When looking at managed switches, there are two types available: smart switches and fully managed switches. Smart switches have a limited number of options for configuration and are ideal for home and office use. Fully managed switches are targeted at servers and enterprises, offering a wide array of tools and features to manage the immediate network.

Unmanaged switches are basic plug-and-play switches with no remote configuration, management or monitoring options, although many can be locally monitored and configured via LED indicators and DIP switches. These inexpensive switches are typically used in small networks, such as home, SOHO or small businesses. In scenarios where the network traffic is light, all that is required is a way for the data to pass from one device to another. In this case there is no need for prioritizing the packets, as all the traffic will flow unimpeded. An unmanaged switch will fill this need without issues.
Managed and unmanaged switches can maintain stability through Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). This protocol can prevent your network from looping endlessly, because it can search for the disconnected device. However, the managed switch is still the best solution for long-range usability and network performance. And it will cover the trends in the near future.

Network Redundancy: Managed switches incorporate Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to provide path redundancy in the network. STP provides redundant paths but prevents loops that are created by multiple active paths between switches, which makes job for a network administrator easier and also proves more profitable for a business.
Remote management: Managed switches use protocols such as or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for monitoring the devices on the network. SNMP helps to collect, organize and modify management information between network devices. So IT administrators can read the SNMP data, and then monitor the performance of the network from a remote location, and detect and repair network problems from a central location without having to physically inspect the switches and devices.
Security and Resilience: Managed switches enable complete control of data, bandwidth and traffic control over the Ethernet network. You can setup additional firewall rules directly into the switch. And managed switches support protocols which allow operators to restrict/control port access.
SFP: The benefit of having multi-rate SFP slots is the network flexible expansion possibility, which allows the user to be able to use 100Mbps and 1Gbps SFP modules for either multi or single-mode fibre optic (or copper) as needed. If requirements change, the SFP module can be replaced and easily protect your switch investment.
Support multiple VLAN as per requirement: Managed switches allow for the creation of multiple VLANs where an 8-port switch functionally can turn into two 4-port switches.
Prioritise bandwidth for data subsets: The switches are able to prioritise one type of traffic over another allowing more bandwidth to be allocated through the network.
- Open ports on unmanaged switches are a security risk
- No resiliency = higher downtime
- Unmanaged switches cannot prioritize traffic
- Unmanaged switches cannot segment network traffic
- Unmanaged switches have limited or no tools for monitoring network activity or performance
After discussing the pros and cons of managed vs. unmanaged switch, we can thus conlude that for end users, network visibility and control can be highly valued in their plants and they are willing to pay for it. Although managed switches are costlier than unmanaged switches, managed switches definitely have more benefits and consistent network performance. When the network requirements may be expanded or better control and monitoring over network traffic is needed, managed switches may be considered.
Related Article: Why Is Managed Switch Good for Business Networks?