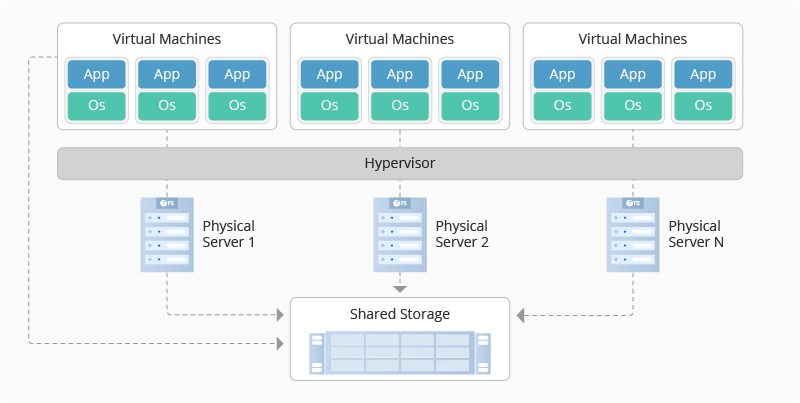
Over the years, the Internet of Things and IoT devices have grown tremendously, effectively boosting productivity and accelerating network agility. This technology has also elevated the adoption of edge computing while ushering in a set of advanced edge devices. By adopting edge computing, computational needs are efficiently met since the computing resources are distributed along the communication path, i.e., via a decentralized computing infrastructure.
One of the benefits of edge computing is improved performance as analytics capabilities are brought closer to the machine. An edge data center also reduces operational costs, thanks to the reduced bandwidth requirement and low latency.
Below, we’ve explored more about 5G wireless systems and multi-access edge computing (MEC), an advanced form of edge computing, and how both extend cloud computing benefits to the edge and closer to the users. Keep reading to learn more.
What Is Multi-Access Edge Computing
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) is a relatively new technology that offers cloud computing capabilities at the network’s edge. This technology works by moving some computing capabilities out of the cloud and closer to the end devices. Hence data doesn’t travel as far, resulting in fast processing speeds.
Ideally, there are two types of MEC, dedicated MEC and distributed MEC. Dedicated MEC is typically deployed at the customer’s site on a mobile private network and is designed only for one business. On the other hand, distributed MEC is deployed on a public network, either 4G or 5G, and connects shared assets and resources.
With both the dedicated and distributed MEC, applications run locally, and data is processed in real or near real-time. This helps avoid latency issues for faster response rates and decision-making. MEC technology has seen wider adoption in video analytics, augmented reality, location services, data caching, local content distribution, etc.
How MEC and 5G are Changing Different Industries
At the heart of multi-access edge computing are wireless and radio access network technologies that open up different networks to a wide range of innovative services. Today, 5G technology is the ultimate network that supports ultra-reliable low latency communication. It also provides an enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) capability for use cases involving significant data rates such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
That said, 5G use cases can be categorized into three domains, massive IoT, mission-critical IoT, and enhanced mobile broadband. Each of the three categories requires different network features regarding security, mobility, bandwidth, policy control, latency, and reliability.
Why MEC Adoption Is on the Rise
5G MEC adoption is growing exponentially, and there are several reasons why this is the case. One reason is that this technology aligns with the distributed and scalable nature of the cloud, making it a key driver of technical transformation. Similarly, MEC technology is a critical business transformation change agent that offers the opportunity to improve service delivery and even support new market verticals.
Among the top use cases driving the high level of 5G, MEC implementation includes video content delivery, the emergence of smart cities, smart utilities (e.g., water and power grids), and connected cars. This also showcases the significant role MEC plays in different IoT domains. Here’s a quick overview of the primary use cases:
- Autonomous vehicles – 5G MEC can help enhance operational functions such as continuous sensing and real-time traffic monitoring. This reduces latency issues and increases bandwidth.
- Smart homes – MEC technology can process data locally, boosting privacy and security. It also reduces communication latency and allows for fast mobility and relocation.
- AR/VR – Moving computational capabilities and processes to edge amplifies the immersive experience to users, plus it extends the battery-life of AR/VR devices.
- Smart energy – MEC resolves traffic congestion issues and delays due to huge data generation and intermittent connectivity. It also reduces cyber-attacks by enforcing security mechanisms closer to the edge.

Getting Started With 5G MEC
One of the key benefits of adopting 5G MEC technology is openness, particularly API openness and the option to integrate third-party apps. Standards compliance and application agility are the other value propositions of multi-access edge computing. Therefore, enterprises looking to benefit from a flexible and open cloud should base their integration on the key competencies they want to achieve.
One of the challenges common during the integration process is hardware platforms’ limitations, as far as scale and openness are concerned. Similarly, deploying 5G MEC technology is costly, especially for small-scale businesses with limited financial backing. Other implementation issues include ecosystem and standards immaturity, software limitations, culture, and technical skillset challenges.
To successfully deploy multi-access edge computing, you need an effective 5G MEC implementation strategy that’s true and tested. You should also consider partnering with an expert IT or edge computing company for professional guidance.
5G MEC Technology: Key Takeaways
Edge-driven transformation is a game-changer in the modern business world, and 5G multi-access edge computing technology is undoubtedly leading the cause. Enterprises that embrace this new technology in their business models benefit from streamlined operations, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experience.
Even then, MEC integration isn’t without its challenges. Companies looking to deploy multi-access edge computing technology should have a solid implementation strategy that aligns with their entire digital transformation agenda to avoid silos.
Article Source: 5G and Multi-Access Edge Computing
Related Articles:
What is Multi-Access Edge Computing?https://community.fs.com/blog/what-is-multi-access-edge-computing.html














 Whether it’s an enterprise or multi-tenant (co-location) facility, the data center is fast becoming an organization’s most valuable strategic asset. Its ability to handle immense volumes of data, provide highly reliable IT services for users and quickly adapt to the increasing demands of a dynamic environment can make or break a business. As a result, IT and facilities professionals are constantly looking to make their data centers more agile and efficient.
Whether it’s an enterprise or multi-tenant (co-location) facility, the data center is fast becoming an organization’s most valuable strategic asset. Its ability to handle immense volumes of data, provide highly reliable IT services for users and quickly adapt to the increasing demands of a dynamic environment can make or break a business. As a result, IT and facilities professionals are constantly looking to make their data centers more agile and efficient. Within the last several years, the market has warmed to the concept of the prefabricated modular data center. A modular data center is a concept that uses prefabricated modules—built and tested at a factory, disassembled, shipped to a site and then reassembled to deliver data center white space, power and cooling infrastructure. A modular data center can be set up and operational within 14 to 20 weeks instead of two to three years. Also, as business capacity needs or technologies change, new modules addressing the change can be quickly and cost-efficiently added or existing solutions pre-engineered for upgrading can be seamlessly modified.
Within the last several years, the market has warmed to the concept of the prefabricated modular data center. A modular data center is a concept that uses prefabricated modules—built and tested at a factory, disassembled, shipped to a site and then reassembled to deliver data center white space, power and cooling infrastructure. A modular data center can be set up and operational within 14 to 20 weeks instead of two to three years. Also, as business capacity needs or technologies change, new modules addressing the change can be quickly and cost-efficiently added or existing solutions pre-engineered for upgrading can be seamlessly modified.