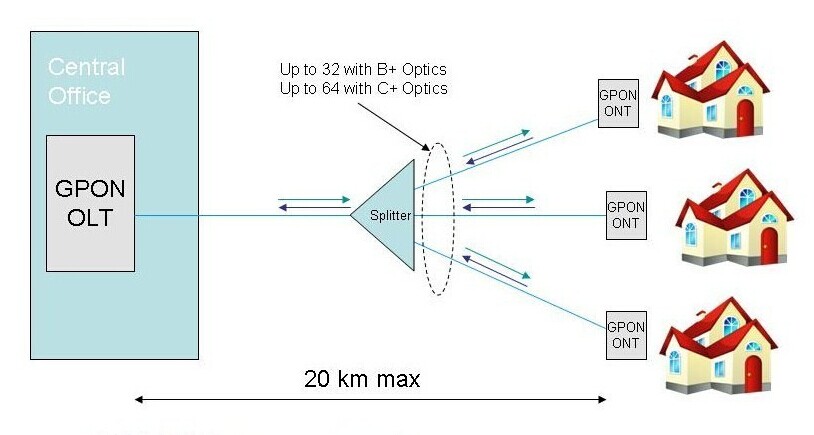
Since the advances in Ethernet technology, “last mile” connectivity is expected to realize between the network backbone and local area networks (end users). Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a cost-effective point-to-multipoint access network, which brings great improvement in data transmission distance (up to 20km) and bandwidth (an downstream capacity of 2.5Gbit/s and an upstream capacity of 1.25Gbit/s ). However, GPON’s higher bandwidth and split ratios are only achievable by using GPON-capable optical transceivers. It is well positioned to help meet the needs for higher bandwidth in FTTx applications, and continues to fuel growth in demand for GPON SFP modules. So this article will introduce the basics of GPON SFP, including GPON OLT, GPON ONU and GPON ONT SFP module.
What Is GPON SFP Module?
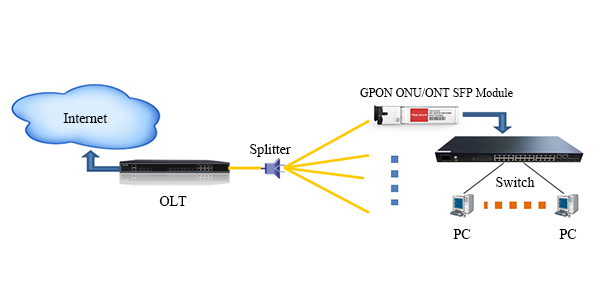
GPON SFP is a new higher-speed bi-directional optical transceiver, which can deliver 2.5 Gbits/sec of bandwidth. And it is a kind of single fiber transceiver which comes with SC connector and can transmit data up to 20km. In addition, it features a 28-dB optical loss budget to enable 1:64 split ratios and provides adequate optical loop lengths. Most EPON and some BPON systems deployed today use 25-dB optics, which limit the split ratio and loop length. For this reason, GPON transceiver enjoys the added advantage of industrial demand. The key performance advantage is to reduce the upstream split loss arising from utilizing the mode-coupled-receivers (MCR) in a PON application. Moreover, this innovative module dose not outweigh the costs over a standard module. For these two reasons, the GPON SFP modules are very attractive to the network operators to improve the utilization of GPON network. On top of that, GPON SFP transceiver is an essential part of GPON system which is necessary both for optical network unit (ONU) installed at the subscriber’s premises and for the optical line terminal (OLT) at the central office (CO). The following part will respectively introduce the GPON OLT, GPON ONU and GPON ONT SFP module.

GPON OLT SFP Module
GPON OLT SFP is designed for OLT side in GPON network. OLT is a equipment integrating L2/L3 switch function, which is located in central office (CO). The main function is to control the information float in both directions: upstream and downstream. The GPON OLT module plays an inevitable role in the upstream and downstream transmission. In order to put across the transmission process, the downstream transmission is taken as an example. A single mode optical fiber coming from OLT (at the central office) PON port, runs to the passive optical splitter (POS) located near end users. And then the optical splitter will divide signals into separate paths which can provide service up to 64 end users. In this basic GPON topology, a GPON OLT module is used to connect a single-mode fiber patch cable to a passive optical splitter. Therefore, GPON OLT transceiver works to get the data, voice and video traffic from metro network or from a long-haul network.

GPON ONU/ONT SFP Module
Since the ONU and ONT are deployed at customer’s premises, they are connected to the OLT by means of optical fiber and no active elements are present in the link. In GPON network, the ONU/ONT transceiver is the physical connection between the customer premises and the central office OLT. This type of modules gets the signals from OLT, so they have the opposite characteristic of GPON OLT transceiver, incorporating a high performance 1310nm burst mode DFB transmitter and 1490nm CW mode APD receiver. By being plugged into advanced “triple play” (data, voice & video) ONT or ONU equipment (with SFP ports), such as Ethernet switches, routers, DSLAMs or home gateway, ONU/ONT SFP module fits seamlessly into existing communications equipment and provides end users with a smooth upgrade to GPON. Therefore, GPON ONU/ONT SFP module plays an important role in the applications for point-to-multipoint (P2MP) ONT / ONU equipment in GPON network.
Conclusion
GPON SFP transceiver meets the the requirements of FTTx network to accelerate the speed or capacity. GPON OLT, ONU and ONT SFP module have their respective roles to play in the GPON networks. Many people may worry the high attenuation losses from optical splitter in the GPON networks, as above mentioned, the GPON optical module is just used to solve this problem in that it utilizes the MCR technology that protects large numbers of signals. In a word, this new module is a compelling network alternative to save cost and increase bandwidth and security.
Related Article: ABC of PON: Understanding OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN