In the field of Ethernet switch connection, link aggregation is a technology to combine multiple ports in parallel between different network switches. It functions to expand bandwidth cost-effectively and to provide redundancy in link failure. However, the umbrella term “link aggregation” is rather a broad terminology containing various conceptions: Link Aggregation Control Protocol, Link Aggregation Group, MLAG, 802.3ad, 802.1AX, etc. Among them the issue of LAG vs LACP confuses many people. Here we introduce LAG vs LACP in sequence and compare LAG vs LACP to illustrate their relationships and differences.
LAG vs LACP: What Is LAG?
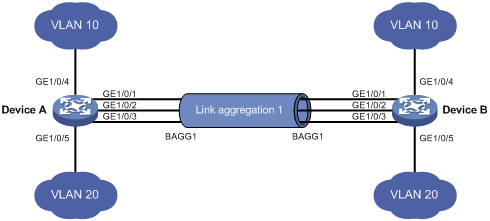
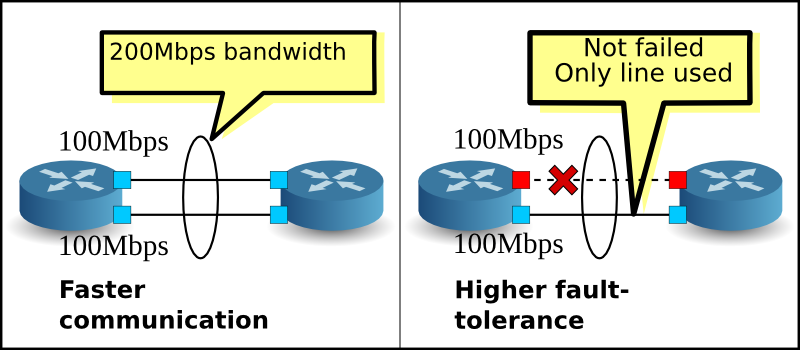
LAG (Link Aggregation Group) is an actual technique or instance for link aggregation. A Link Aggregation Group forms when we connect multiple ports in parallel between two switches and configure them as LAG. As thus LAG builds up multiple links between two switches, which expands bandwidth. Besides, it provides link-level redundancy in network failure and load-balance traffic. Even if one link fails, the remaining links between the two switches will still be running. They also take over those traffic supposed to traverse via the failed one, so data packet won’t get lost.
LAG vs LACP: What Is LACP?
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is a control protocol to set up LAGs automatically. So you can choose to build a static LAG without LACP. Or you can choose to set up a dynamic LAG by using LACP. Simply put, LACP is not a link aggregation instance but a protocol for defining it. LACP enables LAG to transfer from static LAG to dynamic LAG, which allows information exchange of the link aggregation between the LAG component network switches. The information is delivered as packet in Link Aggregation Control Protocol Data Units (LACPDUs). And each port on both switches can be configured to be active or passive via the control protocol to be either preferential to transfer LACPDUs or not.
LAG Implementation Scenario
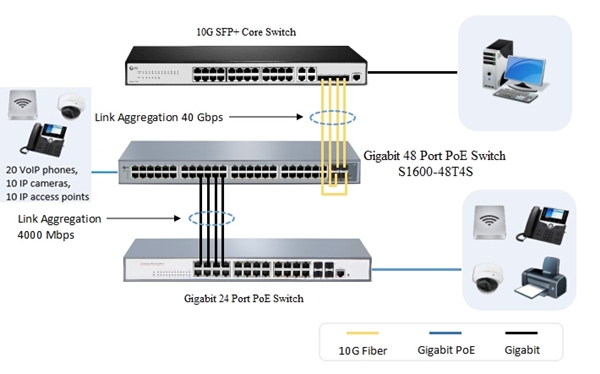
Since LACP is only a protocol for Link Aggregation Group. We’ll omit the LAG vs LACP differentiation to see LAG implementation scenario by FS.COM. Taking the LAG between two gigabit PoE network switches and another 10GbE fiber switch as example. While simply connecting one port on each gigabit PoE switch with one cable, we get 1GE bandwidth. However, when you double link, triple link or higher multiples, the bandwidth will become 2GE, 3GE and so on.
Further, to uplink a backbone core switch, we can use 4 fiber patch cables with corresponding modules to link the 48 port gigabit PoE switch 10GE SFP+ ports and the 10GbE fiber optic switch. Then the uplink bandwidth on the S1600-48T4S expands to 40GE. In the case two LAGs form on the 48 port PoE switch. The link upper limit to form a LAG and the number of LAGs between two switches vary from vendor and switch models.
Figure 1: Linking 4 1GE ports in parallel on FS 48 port PoE switch and 24 port PoE switch to set up a LAG, which boosts bandwidth from 1000Mbps to 4 × 1000Mbps. In this photo two LAGs have been implemented on the FS 48 port PoE switch.
LAG vs LACP : Link Aggregation Advantages to Expand Bandwidth
Whether LAG deploying Link Aggregation Control Protocol or not, it requires no expensive hardware upgrade. Therefore Link Aggregation Group provides a cost-effective solution for bandwidth expansion. Stacking switch is indeed an advanced method to obtain higher bandwidth. However, it is restricted to stackable switch and does not support separate placing. To buy a higher speed switch like a 10GbE switch is also an direct and effective solution. But for ordinary users this hardware upgrade is over budget.
LAG vs LACP: What’s the Difference?
- Link Aggregation Group is a practical instance of link aggregation whereas LACP is a protocol for auto-configuring and maintaining LAG.
- LAG without Link Aggregation Control Protocol is a static configuration, in which each pair of ports in a LAG require manual configuration respectively. However, LACP enabled ports are dynamic configuration, which enable to auto-configure into trunk groups when building LAG.
- When talking about LAG vs LACP, one usually refer to static LAG without LACP vs dynamic LAG with LACP. Generally speaking, dynamic LAG configuration owns advantages over static LAG configuration for automatic failover occur and mutual dynamic configuration. In static link aggregation, LAG cannot detach configuration or cabling errors so as to cause unnecessary network troubles.
Conclusion
LAG vs LACP issue is put forward for the confusing conception between them. LAG is an actual instance for link aggregation. LACP is a control protocol to enable LAG automatically configure network switch ports, detach link failure and activate failover. So LAG encompasses both static LAG configuration and dynamic LAG configuration on the basis of whether employing optional Link Aggregation Control Protocol or not. As a whole, Link Aggregation Group is a cost-effective way to expand bandwidth over switch stacking and other hardware upgrade methods. For minimizing network link failure, LACP enabled dynamic LAG configuration over static LAG is a much better solution to go.