1000BASE-X is a group of standards for Ethernet physical layer standards, which is used for gigabit Ethernet connections that transmit data mainly over fiber optic cable or copper-shielded cable. There are several 1000BASE-X interface types used in SFP transceiver modules, including 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX and 1000BASE-EX. Besides, SFP transceivers are available with different transmitter and receiver types, allowing users to select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the required optical reach over the available optical fiber type (eg: multimode fiber or single-mode fiber). 1000BASE-LX SFP and 1000BASE-SX SFP are two common types of optical transceiver modules in the market. Today’s topic will discuss 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode vs. 1000BASE-LX SFP single-mode.

1000BASE-SX SFP VS. 1000BASE-LX SFP
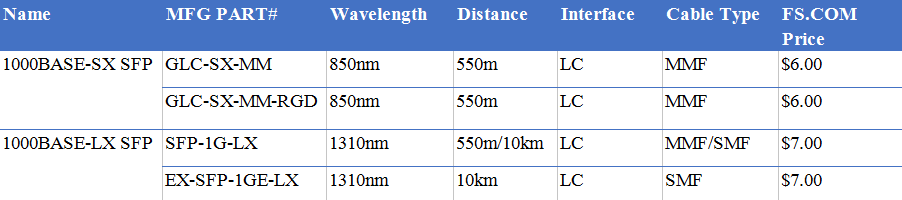
1000BASE-SX is a physical layer specification for Gigabit Ethernet over fiber optic cabling as defined in IEEE 802.3z. The SX systems operate full-duplex with multimode fiber only, using the cheaper 850nm wavelength laser diodes. The maximum distance supported varies between 220 and 550 meters depending on the bandwidth and attenuation of the fiber optic cable used. The standard 1000Base-SX NICs available today are full-duplex and incorporate LC fiber connectors. So 1000BASE-SX SFP supports link length of up to 550m (depending on fiber type) on multimode fiber at 1Gbps. This optic works at 850nm wavelength and uses a LC connector. Take Cisco GLC-SX-MM for example, this 1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver is able to realize 550m link length through OM2 MMF with LC duplex.
As opposed to 1000Base-SX, 1000BASE-LX uses long wavelength laser over both multimode and single-mode fiber. It has a working distance of up to 10 km over single-mode optic fiber, and a maximum length of 550 meters on multimode fiber. So the 1000BASE-LX SFP can operate on standard single-mode fiber optic link spans of up to 10 km, and up to 550 m on any multimode fibers. Arista Networks SFP-1G-LX is 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver that operates over a wavelength of 1310nm for 10 km on SMF and 550m on MMF.
Single-mode SFP VS. Multimode SFP
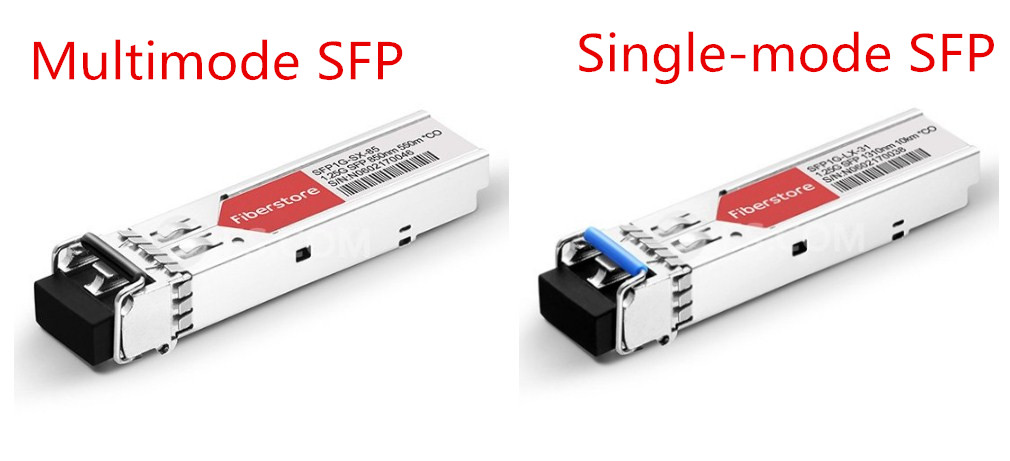
SFP modules can be divided into single-mode SFP and multimode SFP modules. For single-mode SFP modules, there are “LX” for 1310nm and “EX” “EZX” for 1550nm. Single-mode fiber SFP is designed to transmit signals over long distances. So the single-mode module works mainly in the 1310nm and 1550nm wavelengths and is mostly used in a long distances transmission environment reaching 2 km, 10 km, 40 km, 60 km, 80 km and 120 km. For example, Cisco GLC-ZX-SM is a single-mode module, which operates over a wavelength of 1550nm for 80 km.
Single-mode SFP(extraction lever):
- LX – 1310 up to 10km
- EX – 1310 up to 40km
- ZX – 1550 up to 80 km using green ex lever
- EZX – 1550 up to 160 km
NOTE:
- Black color coded bale clasp designates a Multi-mode SFP
- Blue color coded bale clasp designates the 1310nm SFP
Comparatively, multimode SFP transceivers are identified with “SX”. This MMF SFP optics is specially for short distance data transmission. The common multimode SFP modules work in 850nm wavelength and is only used for short distance transmission reaching 100m and 500m. Though it’s not able to transport for long distance, it can transport many kinds of optical signals. For instance, Cisco GLC-SX-MMD is a typical multimode fiber transceiver, which operates over a wavelength of 850nm for 550m.
1000BASE-SX SFP Multimode VS. 1000BASE-LX SFP Single-mode
- Standard
SX stands for short wavelength. The standard specifies a distance capability between 220 meters and 550 meters. The “LX” in 1000BASE-LX stands for long wavelength, indicating that this version of Gigabit Ethernet is intended for use with long-wavelength transmissions (1270 – 1355nm) over long cable runs of fiber optic cabling. 1000BASE-LX can run over both single mode fiber and multimode fiber with a distance of up to 10 km and 550 m, respectively.
- Types of Optical Fibers
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP module will work with single-mode fiber in order to perform both transmission and reception of data. Whereas 1000BASE-SX multimode SFP transceiver will work with multimode fiber, which has a thicker core and allows higher speed at shorter distance.
- Transmission Distance
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP transceivers are mostly used in long distances (up to 10 km) transmission environment. 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode is only used for short distances (up to 550m), like in small area or within the building.
- Wavelength
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP works in 1310nm, whereas 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode works in 850nm.
- Transmission Medium
1000BASE-LX single-mode SFP transport the optical signal for long distance, but there is only one signal in the “tunel”. 1000BASE-SX multimode SFP has many optical signal in one “tunel”, the signals may affect each other. So it can transport many kind of optical signals.
- Dispersion
1000BASE-SX multimode optics are affected by modal dispersion, because the light rays follow different paths through the fiber and arrive at different times on the other end. This is the main reason the distance on this type of optic is limited. Whereas 1000BASE-LX single-mode optics are affected by wave guide dispersion, caused by the light going down the fiber being wider than the core of the fiber. This allows more control of the path of the photons, but is more affected by micro bends, twists and stress on the fiber.
Conclusion
Through 1000BASE-SX SFP multimode vs. 1000BASE-LX SFP single-mode, we could actually conclude that the 1000BASE-SX standard was developed to support lower cost multimode fiber running in horizontal and shorter-length backbone applications, while the 1000BASE-LX standard was developed to support longer-length multimode building fiber backbones and single mode campus backbones. With so many types of SFP modules available in the market, careful notice should be given to the range of differences, including transmission distance, wavelength, cable types, price, etc.
Related Article: The Basics of 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX SFP