In order to meet the increasing system bandwidth needs, local area network (LAN) campus and building backbones, as well as data center backbones, are migrating to higher cabled fiber counts. Ribbon fiber optic cables can offer the highest fiber density relative to cable size, maximize utilization of pathway and spaces and facilitate ease of termination, which makes them an ideal solution for the need. This post mainly focuses on the benefits and applications of ribbon fiber optic cable.
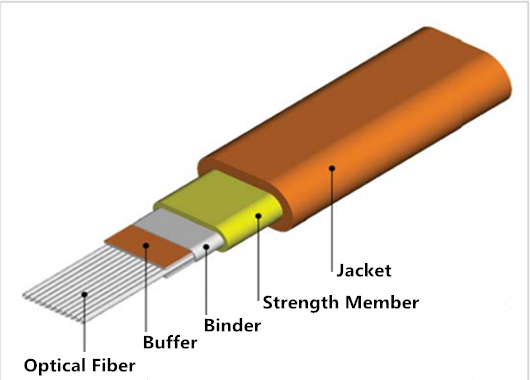
Ribbon fiber optic cable is a type of cable widely deployed in campus, building and data center backbone applications where high fiber counts are required. There are 8 fibers, 12 fibers, 24 fibers and other higher fiber counts available on the market. At present the 12-fiber ribbons are readily accessible and identifiable with ribbon identification numbers and TIA-598 compliant fiber color coding, which make it prevalent in today’s networks. Usually there are two kinds of outer jacket of ribbon fiber optic cables: non-flame-retardant and formulated flame-retardant. The former is often used in outside plant applications, while the latter is typically used for indoor applications. Here is an example of ribbon fiber optic cable construction.
As we all know, stranded loose-tube and ribbon fiber optic cables are staples of the outside plant applications. Both of them perform well in harsh outdoor environments, and both are available in a multitude of configurations, including: all-dielectric, armored, aerial self-supporting, etc. However, when compared to stranded loose-tube cable designs, the ribbon fiber design offers robust performance equivalent to the stranded loose-tube cable, and provides the maximum fiber density relative to cable diameter. The chief distinction between these cables is the manner in which the individual fibers themselves are packaged and managed within the cable. A ribbon fiber cable has the individual fibers precisely bonded together in a matrix that might encompass as few as four or as many as 24 fibers. In contrast, a loose-tube cable has between 2 to 24 individual fibers housed in multiple buffer tubes with each fiber detached from the other.
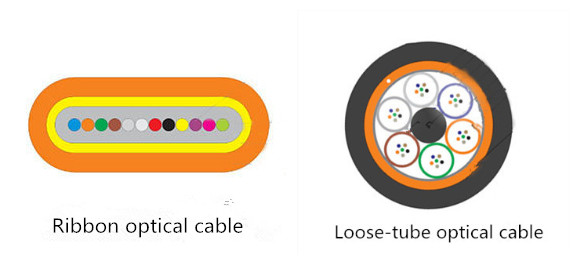
It’s the special ribbon fiber design that makes ribbon fiber optic cable offer more advantages over loose-tube designs in many applications.
- Ribbon fiber optic cable can be prepped and spliced much more rapidly than loose tube cables. That’s means less installation time, less installation labor cost and significantly less emergency restoration time.
- Ribbon fiber optic cables enable a smaller footprint in splice closures and telecommunications room fiber management.
- Ribbon cables offer greater packing density in higher fiber counts which enables more efficient use of limited duct space.
- Ribbon cables are typically very cost competitive in counts above 96 fibers.
Although there are various fiber counts available with ribbon fiber optic cable, the 12-fiber ribbon cables are the most commonly used ones. With the introduction of innovations such as ribbon splitting tools and field-installable 12-fiber array connectors, 12-fiber ribbons are easily terminated with simplex and duplex connectors such as LC or SC connectors or with the MTP connector. The MTP connector is a 12-fiber push/pull optical connector with a footprint similar to the common simplex connector. Many users like to apply MTP connectors to ensure the highest quality connector insertion loss and return loss performance and to expedite the cable installation.
In order to illustrate how ribbon fiber optic cables are deployed, here take the termination of MTP connectorized ribbon cable with patch panel as an example.
The termination is normally used in an interconnect application where a harness assembly is used on the front of the patch panel. We know the MTP fiber cable has 12-fiber MTP connector on one end of the cable and simplex or duplex style connectors on the other end. Just like the picture below shows.

Except for the application noted above, ribbon fiber optic cables also can be used in both interconnect and cross-connect applications where an MTP connector module cassette is used. And they can be applied to pathways and spaces.
Ribbon fiber optic cables deliver high fiber density in the most compact cable package possible. And they also maximize the number of fibers that can be deployed in a limited space while streamlining fiber termination. At the same time they can save time and money with easy mass fusion splicing. Ribbon fiber cable is now easily obtained using traditional simplex or duplex connectors as well as MTP Connectors, which make them suitable for various applications.
