Nowadays, the 40 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) system comes as the popular deployment among some enterprises for their high-performance fiber optic networks. And for 40GbE system, fiber optic transceivers are the indispensable high-capacity modules for multi-lane communications, like 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver. It’s known that 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver has two link options: coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) and parallel single-mode fiber (PSM). How much do you know about them? Can you figure out the differences between them? Following this article and you will get something.
Compliant to 40GBASE-LR4 (eg. QSFP-40G-LR4) of the IEEE P802.3ba standard, this 40GBASE-LR4 CWDM QSFP+ transceiver uses a duplex LC connector as the the optical interface, able to support transmission distance up to 10km over single-mode fiber (SMF) used to minimize the optical dispersion in the long-haul system.
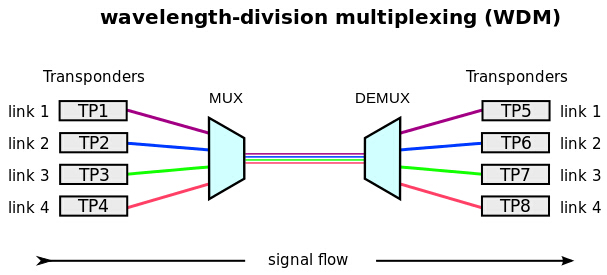
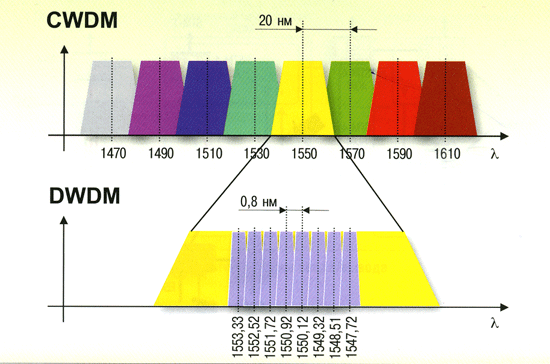
This kind of 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver converts 4 inputs channels of 10G electrical data to 4 CWDM optical signals by a driven 4-wavelength distributed feedback (DFB) laser array, and then multiplexes them into a single channel for 40G optical transmission, propagating out of the transmitter module from the SMF. Reversely, the receiver module accepts the 40G CWDM optical signals input, and demultiplexes it into 4 individual 10G channels with different wavelengths. The central wavelengths of the 4 CWDM channels are 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nm as members of the CWDM wavelength grid defined in ITU-T G694.2. Each wavelength channel is collected by a discrete photo diode and output as electric data after being amplified by a transimpedance amplifier (TIA).

Differently, PSM QSFP+ is a parallel single-mode optical transceiver and uses a MTP/MPO fiber ribbon connector instead of LC. Similarly, PSM QSFP+ also offers 4 independent transmit and receive channels, each capable of 10G operation for an aggregate data rate of 40G with 10km reach over SMF.
In a PSM QSFP+, the transmitter module accepts electrical input signals, while he receiver module converts parallel optical input signals via a photo detector array into parallel electrical output signals. Both the input signals and output signals are compatible with common mode logic (CML) levels.

Allowing for the transceiver module structure, PSM seems more cost effective, since it uses a single uncooled CW laser which splits its output power into four integrated silicon modulators. Additionally, its array-fiber coupling to a MTP connector is relatively simple.
However, when taking the infrastructure into consideration, PSM would be more expensive when the link distance is long, because it uses 8 optical single-mode fibers while CWDM only uses 2 optical single-mode fibers. Besides, in the data center fiber infrastructure, the patch panel has to be changed to accommodate MTP cables, which would cost more than LC connectors and regular SMF cables. Besides, it’s a little difficult to clean MTP connectors. So CWDM is more ideal for 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ link.
For 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceiver link options, both CWDM QSFP+ and PSM QSFP+ support the maximum transmission distance of 10km. The former establishes 40G links over 2 optical SMFs with a duplex LC connector, and the latter achieves 40G links via 8 optical SMFs with a MTP/MPO fiber ribbon connector. Thus no change is required for migration from 10G infrastructure to 40G infrastructure, saving cost when CWDM QSFP+ is chosen. Fiberstore supplies a broad selection of 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceivers which are fully compatible with major brands, such as Finisar (FTL4C1QE1C). For more information about 40GBASE-LR4 QSFP+ transceivers, please visit Fiberstore.