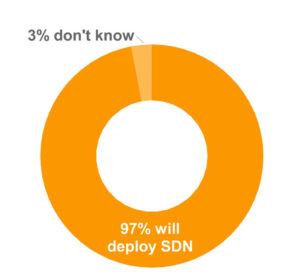
More than a decade ago since the concept of SDN proposed on the heel of OpenFlow, software-defined networking has experienced several year’s research. Until 2012, after Google’s announcement of its backbone network successfully operated on OpenFlow, distributing 12 data centers in the world and increasing WAN utilization from 30% to nearly 100%, OpenFlow had proved its identification as a mature and advanced technology to be applied in the data center networks. Correspondingly SDN networking compliant with programmable feature of OpenFlow protocol become a booming networking technology in the big data centers. What is SDN? What are the advantages brought about by SDN networking? This article may help you to understand.
What Is SDN Networking?
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a technology developed to cater for modern high bandwidth and dynamic applications. It is invented in the historical context to change existing stalled networking infrastructure to a dynamic and manageable one. The core technology is on the basis of OpenFlow protocol to divide software from hardware network device, which makes SDN support software defined functionality. As thus software-defined networking infrastructure becomes more flexible and agile. For instance, SDN networking achieves centralized management by one remote monitoring controller. All network components in the structure such as severs, routers, or Ethernet data switch can be easily added and removed in an efficient way.
What Are the Advantages of SDN Networking?
SDN technology detaches network control from networking hardware devices, making SDN networking directly programmable. Operators can write the SDN program themselves and quickly implement configuration, management, security monitoring and networking optimization. As thus the flexible SDN Networking supports flexible tracking control to adjust traffic agilely and cater for dramatic demands.
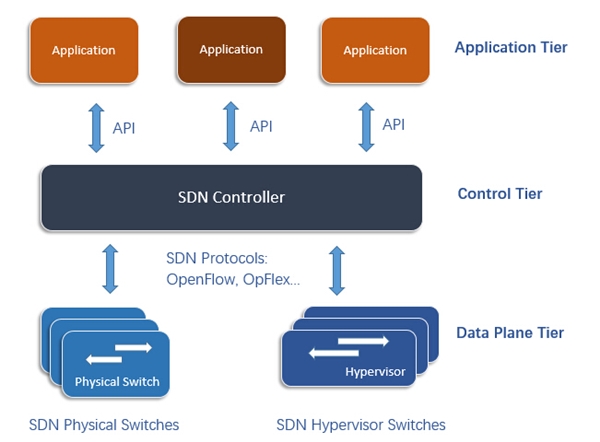
SDN networking deploys a centralized intelligent controller, which programs devices like SDN data switch by software, bridges communication between data devices and applications and displays the network panorama in a virtual switch. It leaves out troubles of differentiating network devices and supports customized control. For instance, in a leaf-spine architecture 10 gigabit switch and 40/ 100GbE switch are deployed in data center different layers. A SDN controller in SDN networking can manage each switch synchronously.
Figure 1: SDN switches and other network applications are controlled and communicated via SDN protocol by a centralized SDN controller in SDN network environment.
What Are the Applications of SDN Networking?
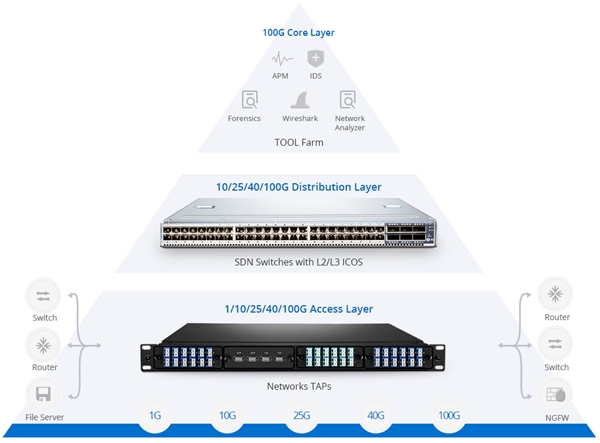
In traditional architecture, reconfiguring a network device is a cumbersome task. Driving by the fast changing Internet business applications, modern networking environment requires for functionality to achieve flexible adjustment. SDN networking meets the need, booming and busting in wide applications. Software-defined networking has developed into three networking branches: software-defined mobile networking (SDMN), software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) and software-defined local area networking (SD-LAN). Overall SDN is frequently used in data center applications. For instance, deploying SDN switch provided by FS.COM such as FS N5850-48S6Q 48 port 10 gigabit switch with 6 QSFP+ 40GbE ports in SDN networking environment can achieve easy flow control and configuration.
Figure 2: Deploying FS 40/100GbE switch in software-defined networking environment as a SDN visibility and security solution.
Conclusion
SDN technology transfers the stagnant situation of internet networking architecture, making SDN networking flexible and agile to business applications. Detaching control functionality from hardware devices (eg. SDN switch), SDN networking achieves quick configuration and management via a centralized SDN controller. Operators can reset an Ethernet switch through SDN protocol in a quick and easy way.