Ethernet cables are classified into sequentially numbered categories (e.g. Cat6, Cat7) according to different specifications. And these categories are how we can easily know what type of cable we need for specific transmission speed, Cat5e Ethernet cable supports up to 1000Mbps, while the latest category Cat8 Ethernet cable can be up to 25/40Gbps. But as for shielded vs unshielded Ethernet cable, how to choose? To find this out, make sure you know the basic information and differences between the two types.
Shielded vs Unshielded Ethernet Cable: Basic Information
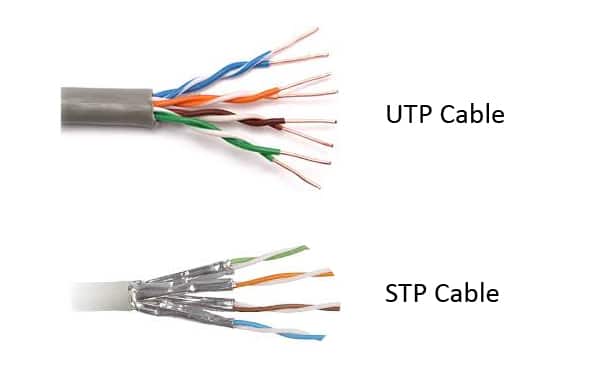
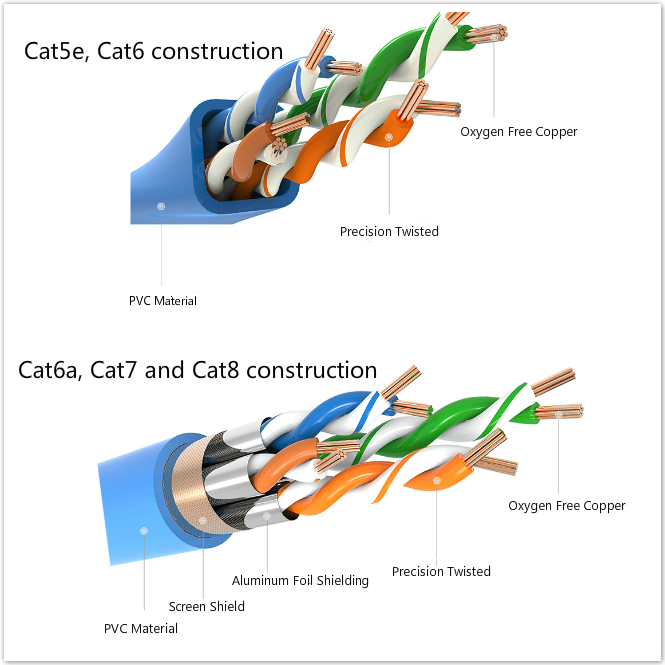
A shielded cable or shield twisted pair (STP) cable has an outside layer or “shield” of conductive material around the internal conductors, which needs to be grounded to cancel the effect of electromagnetic interference (EMI). The conductive shield can reflect or conduct external interference away without affecting the signals of the internal conductor. Therefore, shielded Ethernet cables are usually used to protect signals from EMI over the length of the cable run, so as to result in faster transmission speeds and fewer data errors.
Unshielded means no additional shielding like meshes or aluminum foil are used. Because of this, unshielded Ethernet cables, also called unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable are lighter and cheaper. These Ethernet cables are designed to cancel EMI with the way the pairs are twisted inside the cables. Compared with the shielded cables, unshielded cables provide much less protection. These cables performances are often degraded when EMI is present.
This is a figure of Cat6 shielded and unshielded cable.
Shielded vs Unshielded Ethernet Cable: Difference
The typical difference between the two types lies in the application. Because of the shielding material design, STP and UTP cable will result in different performance. For example, Cat6 shielded and unshielded cable can be up to 10Gbps speed. However, in some cases such as the radio or airports stations, Cat6 UTP cable will experience slower speed and more data transmission errors may be caused when they are close to the machines or other electronics that produce high EMI. But with the additional shielded safeguard, Cat6 STP cable can provide some protection from EMI, performing better than the UTP one. Therefore, STP cables are the best choice for the environments where there is a high chance of electronic interference, while UTP is most suitable for office or home LANs.
In addition, due to the different designs, their cabling grounding methods are different. UTP cables don’t rely on grounding to the same extent as STP cabling. This will decrease the installation time and cost. However, STP needs a more robust grounding and bonding process. And note that the wrong grounded shield actually can worsen crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
Which Should I Choose?
As for shielded vs unshielded Ethernet cable, the best choice should largely depend on where you plan to install the cables. As mentioned above, STP and UTP cables are widely used in different fields due to EMI interference requirement. Airports, medical centres and factories often benefit from STP cabling, because these places need to process numerous machines that produce considerable amounts of interference. On the other hand, for home and office use, it’s wise to choose UTP cables.
Besides, the budget is another factor which may determine the final decision. It’s believed that STP cost much more than UTP since it can provide better protection from EMI. It’s true, but the gap is narrow. For instance, Cat6 Ethernet cable at FS, the Cat6 UTP of 10ft length costs 2.6 dollars while Cat6 shield cable with the same length needs 3.6 dollars, there is only a very small gap, which may be significant for large scale installations, but not for small networks.
Therefore, as for shielded vs unshielded Ethernet cable, it should be determined by the intended application. If you’re still not sure what type of cabling you need, please contact us via sales@fs.com for expert advice.