With the spread of cloud computing and mobile broadband service, the volume of communications traffic has rapidly increased. In order to enable high-capacity optical networks, using a single optical fiber for optical signals of several different wavelengths in DWDM system is widely used. For this reason, tunable transceiver that enables ROADM functionality in next-generation networks is becoming more and more popular. In today’s market, there are mainly two kinds of tunable DWDM transceivers: tunable XFP and tunable SFP+. This article will take you to explore the DWDM C-band tunable XFP transceiver with 40 / 80 km transmission distance options.

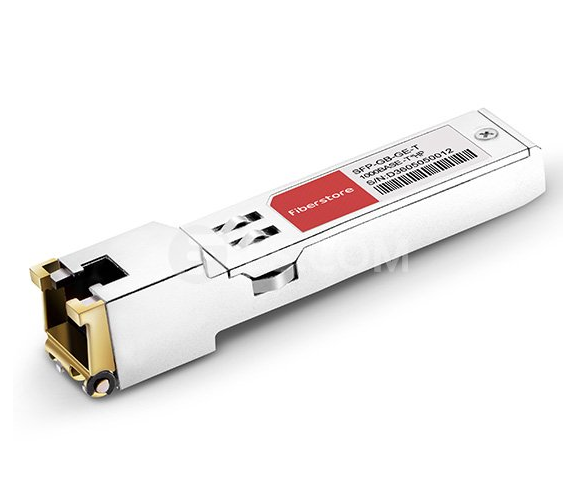
Figure 1: Cisco Compatible Tunable DWDM XFP Transceiver
Tunable XFP Transceiver
Tunable XFP transceiver is an integrated fiber optic transceiver that provides a high-speed serial link at signaling rates from 9.95 Gbps to 11.35 Gbps. It complies with the ITU-T G.698.1 S-D100S1-2D standard with 50GHz channel spacing for SONET/SDH, IEEE DWDM 10GBASE-ZR for 40 or 80 km reach (Ethernet), and DWDM 10G FC (Fibre Channel) for 40 or 80 km reach applications. Tunable DWDM XFP can be tuned from channel C17 (1563.86nm) to C61 (1528.38nm). The maximum distance of this transceiver on a single mode fiber is up to 80 km. As mentioned above, tunable XFP optical transceiver is a full-duplex serial electric, serial optical device with both transmit and receive functions contained in a single module. On the transmit side, the 10 Gbps serial data stream is recovered, retimed, and passed to a modulator driver. The modulator driver biases and modulates a C-band-tunable integrated laser Mach-Zehnder (ILMZ), enabling data transmission over singlemode fiber through an industry-standard LC connector. On the receive side, the 10 Gbps optical data stream is recovered from an APD/transimpedance amplifier, retimed, and passed to an output driver. This module features a hot-pluggable XFI-compliant electrical interface. Here is a simple picture showing its working process.
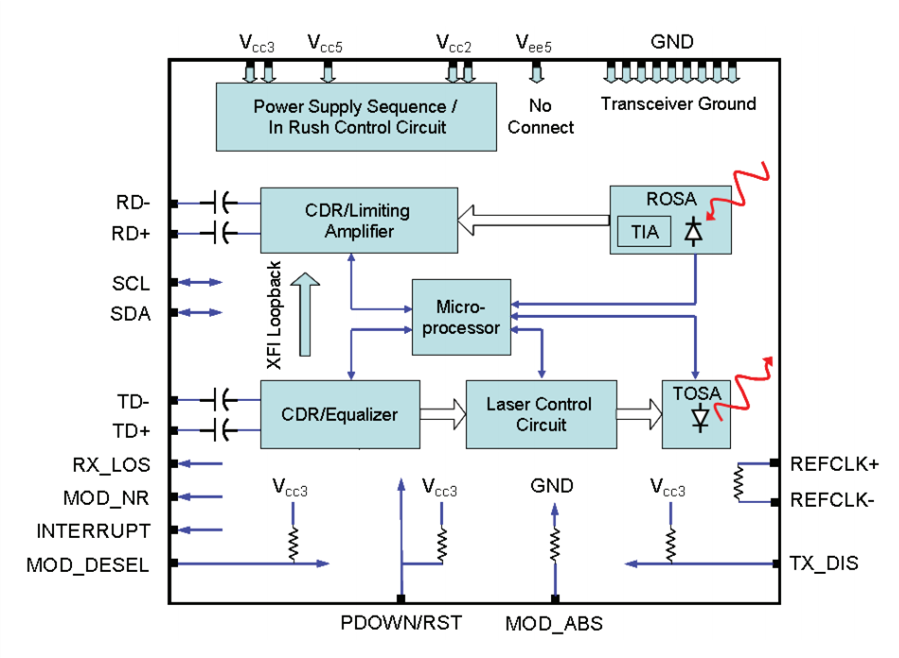
Figure 2: Working Process of Tunable Transceiver
Tunable XFP Optics Specifications:
- 50 GHz ITU channel spacing with intergrated wavelength locker
- Available in all C-Band Wavelengths on the DWDM ITU grid
- Available distances 40 or 80 km
- Supports 9.95Gb/s to 11.35Gb/s
- Built-in Digital Diagnostic Functions
- Tempereature Range: -5°C to 70°C
Two Transmission Distance Options: 40 km or 80 km
There are two transmission distance options for XFP tunable transceiver: 40 km or 80 km. Tunable XFP DWDM 80 km transceiver is designed for long distance optical communications up to 80 km with signaling rates up to 10Gbps. Obviously, the main difference is transmission distance. On account that 10G tunable DWDM XFP optical transceiver provides digital diagnostic functions via a 2-wire serial interface, which allows real-time access to the following operating parameters: transmitted optical power, received optical power, transceiver temperature, laser bias current and transceiver supply voltage. Therefore, the differences between 40 km tunable XFP and 80 km tunable XFP mainly lie on theses parameters. One thing to note is that 40 km tunable XFP optics is designed with high performance PIN receiver, while the 80 km tunable XFP transceiver is APD receiver. The APD (avalanche photodiode) receiver employed in these extended-reach optical transceivers has an enhanced sensitivity to allow for these extended distance fiber runs. However, it is to be noted that the input power is typically between -7 and -24 dBm. Therefore, the receiver sensitivity between these two distance has a big difference. Generally, the max receive dBm of 40 km tunable XFP transceiver is -15, while the 80 km tunable XFP transceiver is -24. And for power budget, 40 km tunable XFP is 14dB while a distance up to 80 km is up to 22dB power budget. The following table lists the main differences.
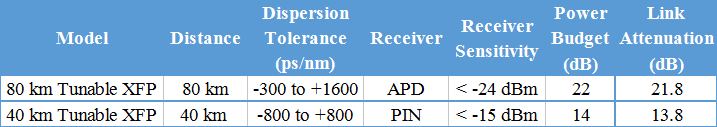
Table 1: 40 km Tunable XFP VS. 80 km Tunable XFP
Conclusion
In general, the channel switching of tunable switches can enable the service operators to turn up circuits faster and reduce their sparing costs dramatically in today’s DWDM systems. On the other hand, tunable optics are usually two or four times more expensive than the regular static DWDM optical module, because a special tunable laser is applied in it. Tunable XFP optical transceiver provides a full C-band window covering 1528nm to 1566nm for DWDM optical networks, which meets the need of rapid increase in the volume of communications traffic from telecom carrier and operator. The tunable DWDM XFP module can replace the fixed DWDM channel XFP transceivers that are currently used, while reduce the large stock since all wavelengths can now be covered with one transceiver module.
| Model | Frequency | Wavelength | Fiber Type | Connector | Price on FS.COM |
| ONS-XC-10G-C | 50 GHz | 1563.86~1528.3 | SMF | LC | $1,400 |
| XFP-10G-CBAND-T50-ZR | 50 GHz | 1563.86~1528.3 | SMF | LC | $1,400 |
| NTK583AAE6 | 50 GHz | 1563.86~1528.3 | SMF | LC | $1,400 |
| TDXFP-10GHXXX-80 | 50 GHz | 1563.86~1528.3 | SMF | LC | $1,400 |
| TDXFP-10GHXXX-40 | 50 GHz | 1563.86~1528.3 | SMF | LC | $1,400 |
Related Article: Wavelength Switching Solution: Tunable XFP Transceiver